Direct interaction between causative genes of DYT1 and DYT6 primary dystonia
- PMID: 20865765
- PMCID: PMC3038652
- DOI: 10.1002/ana.22138
Direct interaction between causative genes of DYT1 and DYT6 primary dystonia
Abstract
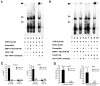
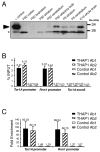
Primary dystonia is a movement disorder characterized by sustained muscle contractions and in which dystonia is the only or predominant clinical feature. TOR1A(DYT1) and the transcription factor THAP1(DYT6) are the only genes identified thus far for primary dystonia. Using electromobility shift assays and chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR), we demonstrate a physical interaction between THAP1 and the TOR1A promoter that is abolished by pathophysiologic mutations. Our findings provide the first evidence that causative genes for primary dystonia intersect in a common pathway and raise the possibility of developing novel therapies targeting this pathway.
Figures

Comment in
-
A molecular link between dystonia 1 and dystonia 6?Ann Neurol. 2010 Oct;68(4):418-20. doi: 10.1002/ana.22183. Ann Neurol. 2010. PMID: 20976763 No abstract available.
References
-
- Fuchs T, Gavarini S, Saunders-Pullman R, et al. Mutations in the THAP1 gene are responsible for DYT6 primary torsion dystonia. Nat Genet. 2009;41:286–288. - PubMed
-
- Djarmati A, Schneider SA, Lohmann K, et al. Mutations in THAP1 (DYT6) and generalised dystonia with prominent spasmodic dysphonia: a genetic screening study. Lancet Neurol. 2009;8:447–452. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

