Dendritic actin filament nucleation causes traveling waves and patches
- PMID: 20867207
- PMCID: PMC2947330
- DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.104.228102
Dendritic actin filament nucleation causes traveling waves and patches
Abstract
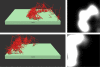
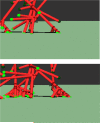
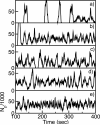
The polymerization of actin via branching at a cell membrane containing nucleation-promoting factors is simulated using a stochastic-growth methodology. The polymerized-actin distribution displays three types of behavior: (a) traveling waves, (b) moving patches, and (c) random fluctuations. Increasing actin concentration causes a transition from patches to waves. The waves and patches move by a treadmilling mechanism not involving myosin II. The effects of downregulation of key proteins on actin wave behavior are evaluated.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
