Resolved sideband emission of InAs/GaAs quantum dots strained by surface acoustic waves
- PMID: 20867805
- PMCID: PMC10198564
- DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.105.037401
Resolved sideband emission of InAs/GaAs quantum dots strained by surface acoustic waves
Abstract
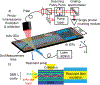
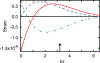
The dynamic response of InAs/GaAs self-assembled quantum dots (QDs) to strain is studied experimentally by periodically modulating the QDs with a surface acoustic wave and measuring the QD fluorescence with photoluminescence and resonant spectroscopy. When the acoustic frequency is larger than the QD linewidth, we resolve phonon sidebands in the QD fluorescence spectrum. Using a resonant pump laser, we have demonstrated optical frequency conversion via the dynamically modulated QD, which is the physical mechanism underlying laser sideband cooling a nanomechanical resonator by means of an embedded QD.
Figures


References
-
- Fry P. et al., Phys. Status Solidi A 178, 269 (2000).
-
- Vogel MM et al., Appl. Phys. Lett 91, 051904 (2007).
-
- Seidl S. et al., Appl. Phys. Lett 88, 203113 (2006).
-
- Itskevich IE et al., Phys. Rev. B 58, R4250 (1998).
-
- Liang Y-H, Arai Y, Ozasa K, Ohashi M, and T suchida E, Physica (Amsterdam) 36E, 1 (2007).
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
