Apoptosis-inducing factor: structure, function, and redox regulation
- PMID: 20868295
- PMCID: PMC3096518
- DOI: 10.1089/ars.2010.3445
Apoptosis-inducing factor: structure, function, and redox regulation
Abstract
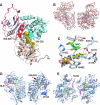
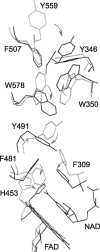
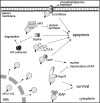
Apoptosis-inducing factor (AIF) is a flavin adenine dinucleotide-containing, NADH-dependent oxidoreductase residing in the mitochondrial intermembrane space whose specific enzymatic activity remains unknown. Upon an apoptotic insult, AIF undergoes proteolysis and translocates to the nucleus, where it triggers chromatin condensation and large-scale DNA degradation in a caspase-independent manner. Besides playing a key role in execution of caspase-independent cell death, AIF has emerged as a protein critical for cell survival. Analysis of in vivo phenotypes associated with AIF deficiency and defects, and identification of its mitochondrial, cytoplasmic, and nuclear partners revealed the complexity and multilevel regulation of AIF-mediated signal transduction and suggested an important role of AIF in the maintenance of mitochondrial morphology and energy metabolism. The redox activity of AIF is essential for optimal oxidative phosphorylation. Additionally, the protein is proposed to regulate the respiratory chain indirectly, through assembly and/or stabilization of complexes I and III. This review discusses accumulated data with respect to the AIF structure and outlines evidence that supports the prevalent mechanistic view on the apoptogenic actions of the flavoprotein, as well as the emerging concept of AIF as a redox sensor capable of linking NAD(H)-dependent metabolic pathways to apoptosis.
Figures






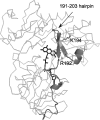

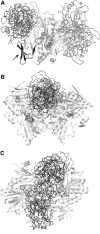


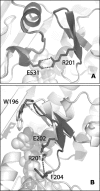

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

