Analysis of lipids from crude lung tissue extracts by desorption electrospray ionization mass spectrometry and pattern recognition
- PMID: 20868645
- PMCID: PMC2980589
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ab.2010.09.017
Analysis of lipids from crude lung tissue extracts by desorption electrospray ionization mass spectrometry and pattern recognition
Abstract
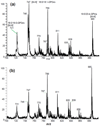
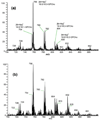
A method is described using desorption electrospray ionization (DESI) mass spectrometry (MS) to obtain phospholipid mass spectral profiles from crude lung tissue extracts. The measured DESI mass spectral lipid fingerprints were then analyzed by unsupervised learning principal components analysis (PCA). This combined approach was used to differentiate the effect(s) of two vaccination routes on lipid composition in mouse lungs. Specifically, the two vaccination routes compared were intranasal (i.n.) and intradermal (i.d.) inoculation of the Francisella tularensis live vaccine strain (Ft-LVS). Lung samples of control and LVS-inoculated mice were quickly extracted with a methanol/chloroform solution, and the crude extract was directly analyzed by DESI-MS, with a total turnaround time of less than 10 min/sample. All of the measured DESI mass spectra (in both positive and negative ion mode) were compared via PCA, resulting in clear differentiation of mass spectral profiles of i.n.-inoculated mouse lung tissues from those of i.d.-inoculated and control mouse lung tissues. Lipid biomarkers responsible for sample differentiation were identified via tandem MS (MS/MS) measurements or by comparison with mass spectra of lipid standards. The DESI-MS approach described here provided a practical and rapid means to analyze tissue samples without extensive extractions and solvent changes.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




References
-
- Ferguson JR. Biological Weapons and U.S. Law. J. Amer. Med. Assoc. 1997;278:357–360. - PubMed
-
- Wayne Conlan J, Shen H, KuoLee R, Zhao X, Chen W. Aerosol-, but not intradermal-immunization with the live vaccine strain of Francisella tularens1is protects mice against subsequent aerosol challenge with a highly virulent type A strain of the pathogen by an αβ T cell- and interferon gamma- dependent mechanism. Vaccine. 2005;23:2477–2485. - PubMed
-
- Koumanov KS, Tessier C, Momchilova AB, Rainteau D, Wolf C, Quinn PJ. Comparative lipid analysis and structure of detergent-resistant membrane raft fractions isolated from human and ruminant erythrocytes. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics. 2005;434:150–158. - PubMed
-
- Postle AD, Heeley EL, Wilton DC. A comparison of the molecular species compositions of mammalian lung surfactant phospholipids. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 2001;129A(Part A):65–73. Molecular & Integrative Physiology. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

