Targeting cyclooxygenases-1 and -2 in neuroinflammation: Therapeutic implications
- PMID: 20868723
- PMCID: PMC3008299
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biochi.2010.09.009
Targeting cyclooxygenases-1 and -2 in neuroinflammation: Therapeutic implications
Abstract
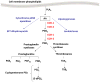
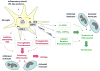
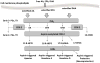
Neuroinflammation has been implicated in the pathogenesis or the progression of a variety of acute and chronic neurological and neurodegenerative disorders, including Alzheimer's disease. Prostaglandin H synthases or cyclooxygenases (COX -1 and COX-2) play a central role in the inflammatory cascade by converting arachidonic acid into bioactive prostanoids. In this review, we highlighted recent experimental data that challenge the classical view that the inducible isoform COX-2 is the most appropriate target to treat neuroinflammation. First, we discuss data showing that COX-2 activity is linked to anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective actions and is involved in the generation of novel lipid mediators with pro-resolution properties. Then, we review recent data demonstrating that COX-1, classically viewed as the homeostatic isoform, is actively involved in brain injury induced by pro-inflammatory stimuli including Aβ, lipopolysaccharide, IL-1β, and TNF-α. Overall, we suggest revisiting the traditional views on the roles of each COX during neuroinflammation and we propose COX-1 inhibition as a viable therapeutic approach to treat CNS diseases with a marked inflammatory component.
Published by Elsevier Masson SAS.
Figures
References
-
- Kis B, Snipes JA, Busija DW. Acetaminophen and the cyclooxygenase-3 puzzle: sorting out facts, fictions, and uncertainties. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2005;315:1–7. - PubMed
-
- O’Banion MK. Cyclooxygenase-2: molecular biology, pharmacology, and neurobiology. Crit Rev Neurobiol. 1999;13:45–82. - PubMed
-
- Morita I. Distinct functions of COX-1 and COX-2. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2002;68–69:165–175. - PubMed
-
- Funk CD, FitzGerald GA. COX-2 inhibitors and cardiovascular risk. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2007;50:470–479. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

