Acetylation of tau inhibits its degradation and contributes to tauopathy
- PMID: 20869593
- PMCID: PMC3035103
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2010.08.044
Acetylation of tau inhibits its degradation and contributes to tauopathy
Erratum in
- Neuron. 2010 Nov 18;68(4):801
Abstract
Neurodegenerative tauopathies characterized by hyperphosphorylated tau include frontotemporal dementia and Parkinsonism linked to chromosome 17 (FTDP-17) and Alzheimer's disease (AD). Reducing tau levels improves cognitive function in mouse models of AD and FTDP-17, but the mechanisms regulating the turnover of pathogenic tau are unknown. We found that tau is acetylated and that tau acetylation prevents degradation of phosphorylated tau (p-tau). We generated two antibodies specific for acetylated tau and showed that tau acetylation is elevated in patients at early and moderate Braak stages of tauopathy. Histone acetyltransferase p300 was involved in tau acetylation and the class III protein deacetylase SIRT1 in deacetylation. Deleting SIRT1 enhanced levels of acetylated-tau and pathogenic forms of p-tau, probably by blocking proteasome-mediated degradation. Inhibiting p300 with a small molecule promoted tau deacetylation and eliminated p-tau associated with tauopathy. Modulating tau acetylation could be a new therapeutic strategy to reduce tau-mediated neurodegeneration.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

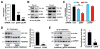
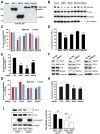

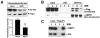



Comment in
-
Acetylation unleashes protein demons of dementia.Neuron. 2010 Sep 23;67(6):900-2. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2010.09.010. Neuron. 2010. PMID: 20869587
References
-
- Amos LA. Microtubule structure and its stabilisation. Org Biomol Chem. 2004;2:2153–2160. - PubMed
-
- Ballatore C, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ. Tau-mediated neurodegeneration in Alzheimer's disease and related disorders. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2007;8:663–672. - PubMed
-
- Braak H, Braak E. Neuropathological stageing of Alzheimer-related changes. Acta Neuropathol Berl. 1991;82:239–259. - PubMed
-
- Cairns NJ, Bigio EH, Mackenzie IR, Neumann M, Lee VM, Hatanpaa KJ, White CL, 3rd, Schneider JA, Grinberg LT, Halliday G, et al. Neuropathologic diagnostic and nosologic criteria for frontotemporal lobar degeneration: consensus of the Consortium for Frontotemporal Lobar Degeneration. Acta Neuropathol. 2007;114:5–22. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

