Too much or not enough of a good thing? Cardiac glucolipotoxicity versus lipoprotection
- PMID: 20869969
- PMCID: PMC3019257
- DOI: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2010.09.014
Too much or not enough of a good thing? Cardiac glucolipotoxicity versus lipoprotection
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest to disclose related to this paper.
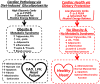
Figures
References
-
- Kessler D. The End of Overeating. New York: Rodale; 2009.
-
- [Accessed July 29, 2009]. http://thinkexist.com/quotation/what_nourishes_me_also_destroys_me/33385....
-
- Park SY, Cho YR, Finck BN, Kim HJ, Higashimori T, Hong EG, et al. Cardiac-specific overexpression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-alpha causes insulin resistance in heart and liver. Diabetes. 2005;54:2514–24. - PubMed
-
- Sharma S, Adrogue JV, Golfman L, Uray I, Lemm J, Youker K, et al. Intramyocardial lipid accumulation in the failing human heart resembles the lipotoxic rat heart. FASEB J. 2004;18:1692–700. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

