Disruption of thyroid hormone receptor-mediated transcription and thyroid hormone-induced Purkinje cell dendrite arborization by polybrominated diphenyl ethers
- PMID: 20870570
- PMCID: PMC3040602
- DOI: 10.1289/ehp.1002065
Disruption of thyroid hormone receptor-mediated transcription and thyroid hormone-induced Purkinje cell dendrite arborization by polybrominated diphenyl ethers
Abstract
Background: Polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) have been used as flame retardants and are becoming a ubiquitous environmental contaminant. Adverse effects in the developing brain are of great health concern.
Objective: We investigated the effect of PBDEs/hydroxylated PBDEs (OH-PBDEs) on thyroid hormone (TH) receptor (TR)-mediated transcription and on TH-induced dendrite arborization of cerebellar Purkinje cells.
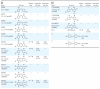
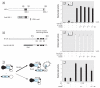
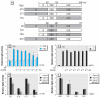
Methods: We examined the effect of PBDEs/OH-PBDEs on TR action using a transient transfection-based reporter gene assay. TR-cofactor binding was studied by the mammalian two-hybrid assay, and TR-DNA [TH response element (TRE)] binding was examined by the liquid chemiluminescent DNA pull-down assay. Chimeric receptors generated from TR and glucocorticoid receptor (GR) were used to identify the functional domain of TR responsible for PBDE action. The change in dendrite arborization of the Purkinje cell in primary culture of newborn rat cerebellum was also examined.
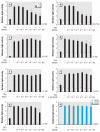
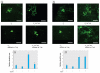
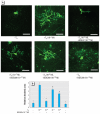
Results: Several PBDE congeners suppressed TR-mediated transcription. The magnitude of suppression correlated with that of TR-TRE dissociation. PBDEs suppressed transcription of chimeric receptors containing the TR DNA binding domain (TR-DBD). We observed no such suppression with chimeras containing GR-DBD. In the cerebellar culture, PBDE significantly suppressed TH-induced Purkinje cell dendrite arborization.
Conclusions: Several PBDE congeners may disrupt the TH system by partial dissociation of TR from TRE acting through TR-DBD and, consequently, may disrupt normal brain development.
Figures
Comment in
-
Thyroid hormone understanding branches out: insights into PBDE impacts on brain development.Environ Health Perspect. 2011 Feb;119(2):A80-1. doi: 10.1289/ehp.119-a80a. Environ Health Perspect. 2011. PMID: 21285014 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Branchi I, Capone F, Alleva E, Costa LG. Polybrominated diphenyl ethers: neurobehavioral effects following developmental exposure. Neurotoxicology. 2003;24:449–462. - PubMed
-
- Carey M, Kakidani H, Leatherwood J, Mostashari F, Ptashne M. An amino-terminal fragment of GAL4 binds DNA as a dimer. J Mol Biol. 1989;209:423–432. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
