Lysosomal fusion and SNARE function are impaired by cholesterol accumulation in lysosomal storage disorders
- PMID: 20871593
- PMCID: PMC2982760
- DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2010.237
Lysosomal fusion and SNARE function are impaired by cholesterol accumulation in lysosomal storage disorders
Erratum in
-
Lysosomal fusion and SNARE function are impaired by cholesterol accumulation in lysosomal storage disorders.EMBO J. 2022 Dec 1;41(23):e112402. doi: 10.15252/embj.2022112402. Epub 2022 Nov 2. EMBO J. 2022. PMID: 36321514 Free PMC article.
Abstract
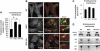
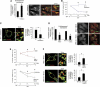
The function of lysosomes relies on the ability of the lysosomal membrane to fuse with several target membranes in the cell. It is known that in lysosomal storage disorders (LSDs), lysosomal accumulation of several types of substrates is associated with lysosomal dysfunction and impairment of endocytic membrane traffic. By analysing cells from two severe neurodegenerative LSDs, we observed that cholesterol abnormally accumulates in the endolysosomal membrane of LSD cells, thereby reducing the ability of lysosomes to efficiently fuse with endocytic and autophagic vesicles. Furthermore, we discovered that soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor attachment protein (SNAP) receptors (SNAREs), which are key components of the cellular membrane fusion machinery are aberrantly sequestered in cholesterol-enriched regions of LSD endolysosomal membranes. This abnormal spatial organization locks SNAREs in complexes and impairs their sorting and recycling. Importantly, reducing membrane cholesterol levels in LSD cells restores normal SNARE function and efficient lysosomal fusion. Our results support a model by which cholesterol abnormalities determine lysosomal dysfunction and endocytic traffic jam in LSDs by impairing the membrane fusion machinery, thus suggesting new therapeutic targets for the treatment of these disorders.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Cao Y, Espinola JA, Fossale E, Massey AC, Cuervo AM, MacDonald ME, Cotman SL (2006) Autophagy is disrupted in a knock-in mouse model of juvenile neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis. J Biol Chem 281: 20483–20493 - PubMed
-
- Diettrich O, Mills K, Johnson AW, Hasilik A, Winchester BG (1998) Application of magnetic chromatography to the isolation of lysosomes from fibroblasts of patients with lysosomal storage disorders. FEBS Lett 441: 369–372 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

