Pharmacological inhibition of EGFR signaling enhances G-CSF-induced hematopoietic stem cell mobilization
- PMID: 20871610
- PMCID: PMC4464748
- DOI: 10.1038/nm.2217
Pharmacological inhibition of EGFR signaling enhances G-CSF-induced hematopoietic stem cell mobilization
Abstract
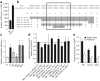
Mobilization of hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells (HSPCs) from bone marrow into peripheral blood by the cytokine granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) has become the preferred source of HSPCs for stem cell transplants. However, G-CSF fails to mobilize sufficient numbers of stem cells in up to 10% of donors, precluding autologous transplantation in those donors or substantially delaying transplant recovery time. Consequently, new regimens are needed to increase the number of stem cells in peripheral blood upon mobilization. Using a forward genetic approach in mice, we mapped the gene encoding the epidermal growth factor receptor (Egfr) to a genetic region modifying G-CSF-mediated HSPC mobilization. Amounts of EGFR in HSPCs inversely correlated with the cells' ability to be mobilized by G-CSF, implying a negative role for EGFR signaling in mobilization. In combination with G-CSF treatment, genetic reduction of EGFR activity in HSPCs (in waved-2 mutant mice) or treatment with the EGFR inhibitor erlotinib increased mobilization. Increased mobilization due to suppression of EGFR activity correlated with reduced activity of cell division control protein-42 (Cdc42), and genetic Cdc42 deficiency in vivo also enhanced G-CSF-induced mobilization. Our findings reveal a previously unknown signaling pathway regulating stem cell mobilization and provide a new pharmacological approach for improving HSPC mobilization and thereby transplantation outcomes.
Figures
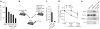
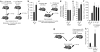
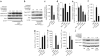
Comment in
-
Stem cells on the move.Nat Med. 2010 Oct;16(10):1073-4. doi: 10.1038/nm1010-1073. Nat Med. 2010. PMID: 20930742 No abstract available.
-
Vagrant stem cells draft their gene companions.Cell Stem Cell. 2010 Nov 5;7(5):547-8. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2010.10.006. Cell Stem Cell. 2010. PMID: 21040892 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Cdc42 inhibitor ML141 enhances G-CSF-induced hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell mobilization.Int J Hematol. 2015 Jan;101(1):5-12. doi: 10.1007/s12185-014-1690-z. Epub 2014 Oct 15. Int J Hematol. 2015. PMID: 25315193
-
HIF-1α-stabilizing agent FG-4497 rescues human CD34+ cell mobilization in response to G-CSF in immunodeficient mice.Exp Hematol. 2017 Aug;52:50-55.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.exphem.2017.05.004. Epub 2017 May 17. Exp Hematol. 2017. PMID: 28527810
-
Adrenaline administration promotes the efficiency of granulocyte colony stimulating factor-mediated hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell mobilization in mice.Int J Hematol. 2013 Jan;97(1):50-7. doi: 10.1007/s12185-012-1228-1. Epub 2012 Dec 8. Int J Hematol. 2013. PMID: 23224606
-
Mechanisms of G-CSF-mediated hematopoietic stem and progenitor mobilization.Leukemia. 2011 Feb;25(2):211-7. doi: 10.1038/leu.2010.248. Epub 2010 Nov 16. Leukemia. 2011. PMID: 21079612 Review.
-
Cytokine-induced hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell mobilization: unraveling interactions between stem cells and their niche.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2020 Apr;1466(1):24-38. doi: 10.1111/nyas.14059. Epub 2019 Apr 21. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2020. PMID: 31006885 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Chemical approaches to stem cell biology and therapeutics.Cell Stem Cell. 2013 Sep 5;13(3):270-83. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2013.08.002. Cell Stem Cell. 2013. PMID: 24012368 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of the RhoGTPase Cdc42 by ML141 enhances hepatocyte differentiation from human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells via the Wnt5a/PI3K/miR-122 pathway: impact of the age of the donor.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018 Jun 19;9(1):167. doi: 10.1186/s13287-018-0910-5. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018. PMID: 29921325 Free PMC article.
-
Epidermal Growth Factor and Granulocyte Colony Stimulating Factor Signaling Are Synergistic for Hematopoietic Regeneration.Stem Cells. 2018 Feb;36(2):252-264. doi: 10.1002/stem.2731. Epub 2017 Nov 10. Stem Cells. 2018. PMID: 29086459 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping Bone Marrow Response in the Vertebral Column by Positron Emission Tomography Following Radiotherapy and Erlotinib Therapy of Lung Cancer.Mol Imaging Biol. 2019 Apr;21(2):391-398. doi: 10.1007/s11307-018-1226-7. Mol Imaging Biol. 2019. PMID: 29916117
-
EGFR-Stat3 signalling in nerve glial cells modifies neurofibroma initiation.Oncogene. 2017 Mar 23;36(12):1669-1677. doi: 10.1038/onc.2016.386. Epub 2016 Oct 17. Oncogene. 2017. PMID: 27748759 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Katayama Y, et al. Signals from the sympathetic nervous system regulate hematopoietic stem cell egress from bone marrow. Cell. 2006;124:407–421. - PubMed
-
- Adams GB, et al. Therapeutic targeting of a stem cell niche. Nat Biotechnol. 2007;25:238–243. - PubMed
-
- Carlo-Stella C, et al. Use of recombinant human growth hormone (rhGH) plus recombinant human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (rhG-CSF) for the mobilization and collection of CD34+ cells in poor mobilizers. Blood. 2004;103:3287–3295. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

