A Parent-Targeted Intervention for Adolescent Substance Use Prevention: Lessons Learned
- PMID: 20871746
- PMCID: PMC2944654
- DOI: 10.1177/0193841X9501900203
A Parent-Targeted Intervention for Adolescent Substance Use Prevention: Lessons Learned
Abstract
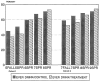
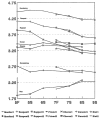
This controlled parent-targeted drug prevention intervention followed two cohorts of students to determine the effect of encouraging parents to intervene in risk factors for adolescent tobacco and alcohol use. Suggestions included limiting association with substance-using peers and asking parents to limit adolescent access to alcohol. Although student participation and retention in the study was good parent participation was poor. Parents were unlikely to know whether their children had substance-using friends and there was no impact on adolescent substance use. However, parent monitoring of children's whereabouts, maintaining high rapport and a respectful parent-child relationship did protect against adolescent substance use. Future parent-targeted prevention programs should target protective factors, rather than trying to control risk factors.
Figures









References
-
- Albert WG, Simpson RI, Eaglesham JA. Evaluation of a drinking and parenting educational program in six Ontario communities. Journal of Drug Education. 1983;13(4):327–35.
-
- Bangert-Drown RL. The effects of school-based substance abuse education—a meta-analysis. Journal of Drug Education. 1988;18:243–65. - PubMed
-
- Baumrind D. The influence of parenting style on adolescent competence and substance use. Journal of Early Adolescence. 1991;11:56–95.
-
- Botvin GJ, Wills T. Personal and social skills training, Cognitive-behavioral approaches to substance abuse prevention. In: Bell C, Battjes R, editors. Prevention research deterring drug abuse among children and adolescents. Washington, DC: U.S. Government Printing Office; 1985. pp. 8–49. NIDA Research Monograph No. 56 DHHS Publication No. ADM 85-1. - PubMed
-
- Brown JH, Horowitz JE. Deviance and deviants. Evaluation Review. 1993;17(5):520–55.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

