Antiamnesic effect of stevioside in scopolamine-treated rats
- PMID: 20871768
- PMCID: PMC2937318
- DOI: 10.4103/0253-7613.66840
Antiamnesic effect of stevioside in scopolamine-treated rats
Abstract
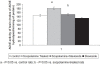
The present study was undertaken to explore the potential of stevioside in memory dysfunction of rats. Memory impairment was produced by scopolamine (0.5 mg/kg, i.p.) in animals. Morris water maze (MWM) test was employed to assess learning and memory. Brain acetylcholinestrase enzyme (AChE) activity was measured to assess the central cholinergic activity. The levels of brain thiobarbituric acid-reactive species (TBARS) and reduced glutathione (GSH) were estimated to assess the degree of oxidative stress. Scopolamine administration induced significant impairment of learning and memory in rats, as indicated by a marked decrease in MWM performance. Scopolamine administration also produced a significant enhancement of brain AChE activity and brain oxidative stress (increase in TBARS and decrease in GSH) levels. Pretreatment of stevioside (250 mg/kg dose orally) significantly reversed scopolamine-induced learning and memory deficits along with attenuation of scopolamine-induced rise in brain AChE activity and brain oxidative stress levels. It may be concluded that stevioside exerts a memory-preservative effect in cognitive deficits of rats possibly through its multiple actions.
Keywords: Memory; Morris water-maze; scopolamine; stevioside.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
Effects of erythropoietin on memory deficits and brain oxidative stress in the mouse models of dementia.Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2010 Oct;14(5):345-52. doi: 10.4196/kjpp.2010.14.5.345. Epub 2010 Oct 31. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 21165335 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprotective effect of Cubebin: A dibenzylbutyrolactone lignan on scopolamine-induced amnesia in mice.Indian J Med Res. 2017 Aug;146(2):255-259. doi: 10.4103/ijmr.IJMR_156_14. Indian J Med Res. 2017. PMID: 29265027 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological Evaluation of the Recuperative Effect of Morusin Against Aluminium Trichloride (AlCl3)-Induced Memory Impairment in Rats.Cent Nerv Syst Agents Med Chem. 2017;17(3):196-200. doi: 10.2174/1871524917666161111095335. Cent Nerv Syst Agents Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 27834136
-
Dendrobium nobile Lindl ameliorates learning and memory deficits in scopolamine-treated mice.J Ethnopharmacol. 2024 Apr 24;324:117416. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2023.117416. Epub 2023 Nov 21. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 37981114
-
Evaluation of Cucurbita maxima extract against scopolamine-induced amnesia in rats: implication of tumour necrosis factor alpha.Z Naturforsch C J Biosci. 2014 Sep-Oct;69(9-10):407-17. doi: 10.5560/znc.2014-0003. Z Naturforsch C J Biosci. 2014. PMID: 25711042
Cited by
-
Role of central angiotensin receptors in scopolamine-induced impairment in memory, cerebral blood flow, and cholinergic function.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2012 Jul;222(2):185-202. doi: 10.1007/s00213-012-2639-7. Epub 2012 Feb 24. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2012. PMID: 22362194
-
Ameliorative effect of carveol on scopolamine-induced memory impairment in rats.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2022 Dec;25(12):1504-1512. doi: 10.22038/IJBMS.2022.66797.14647. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2022. PMID: 36544525 Free PMC article.
-
Treadmill exercise ameliorates short-term memory disturbance in scopolamine-induced amnesia rats.Int Neurourol J. 2014 Mar;18(1):16-22. doi: 10.5213/inj.2014.18.1.16. Epub 2014 Mar 31. Int Neurourol J. 2014. PMID: 24729923 Free PMC article.
-
Treadmill exercise ameliorates disturbance of spatial learning ability in scopolamine-induced amnesia rats.J Exerc Rehabil. 2014 Jun 30;10(3):155-61. doi: 10.12965/jer.140110. eCollection 2014 Jun. J Exerc Rehabil. 2014. PMID: 25061594 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological investigation of Achras sapota against scopolamine induce amnesia and cognitive impairment in laboratory animals.Toxicol Rep. 2024 Nov 19;13:101813. doi: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2024.101813. eCollection 2024 Dec. Toxicol Rep. 2024. PMID: 39669746 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fratiglioni L, Winblad B, Strauss EV. Prevention of Alzheimer’s disease and dementia.Major findings from the Kungsholmen Project. Physiol Behav. 2007;92:98–104. - PubMed
-
- Kawamata T, Katayam Y, Meda T, Mori T, Aoyama N, Kikuchi T, et al. Antioxidant OPC-14117, attenuates edema formation and behavioral deficits following cortical contusion in rats. Acta Neurochir Suppl. 2005;70:191–3. - PubMed
-
- Prasad KN, William CC, Prasad KC. Risk factors for Alzheimer’s disease: Role of multiple antioxidants, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory and cholinergic agents alone or in combination in prevention and treatment. J Am Coll Nutr. 2002;21:506–22. - PubMed
-
- Hanson JR, De Oliveira BH. Stevioside and related sweet diterpenoid glycosides. Nat Prod Rep. 1993;10:301–9. - PubMed
-
- Chatsudthipong V, Muanprasat C. Stevioside and related compounds: Therapeutic benefits beyond sweetness. Pharmacol Ther. 2009;121:41–54. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

