Serum KL-6 levels in lung cancer patients with or without interstitial lung disease
- PMID: 20872562
- PMCID: PMC6647714
- DOI: 10.1002/jcla.20404
Serum KL-6 levels in lung cancer patients with or without interstitial lung disease
Abstract
Background: It is not known whether lung cancer patients with interstitial lung disease (ILD) might have higher serum levels of KL-6, a high molecular weight glycoprotein classified as a polymorphic epithelial mucin. In addition, prognosis of these patients with elevated serum KL-6 levels might be poorer than that with normal KL-6 levels, but it has not been well clarified.
Methods: Serum KL-6 levels in 273 lung cancer patients with or without ILD, and prognostic significance of elevated serum KL-6 levels in these patients were studied using uni- and multivariate analyses.
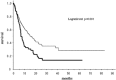
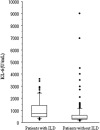
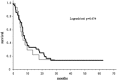
Results: Serum KL-6 levels were elevated (>500 U/ml) in 73.5% of lung cancer patients with ILD and in 33.7% of those without ILD. Serum KL-6 levels in lung cancer patients with ILD were significantly higher than those without ILD. In lung cancer patients with ILD, elevated serum KL-6 has no prognostic significance, but in those without ILD, however, it was one of the unfavorable prognostic factors.
Conclusions: Elevated serum KL-6 levels can be observed in lung cancer patients both with and without ILD. Having ILD has strong prognostic impact in patients with lung cancer. In those without ILD, however, elevated KL-6 levels may be related to poor prognosis.
J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 24:295-299, 2010. © 2010 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Prognostic significance of preoperative serum Krebs von den Lungen-6 level in non-small cell lung cancer.Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2016 Nov;64(11):657-661. doi: 10.1007/s11748-016-0706-4. Epub 2016 Aug 11. Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2016. PMID: 27515028
-
Circulating markers of interstitial lung disease and subsequent risk of lung cancer.Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2011 Oct;20(10):2262-72. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-11-0326. Epub 2011 Aug 9. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2011. PMID: 21828236 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Serum KL-6 levels reflect the severity of interstitial lung disease caused by immune checkpoint inhibitors.Immunobiology. 2025 Jan;230(1):152866. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2024.152866. Epub 2025 Jan 5. Immunobiology. 2025. PMID: 39798404
-
Utility of KL-6/MUC1 in the clinical management of interstitial lung diseases.Respir Investig. 2012 Mar;50(1):3-13. doi: 10.1016/j.resinv.2012.02.001. Epub 2012 Mar 8. Respir Investig. 2012. PMID: 22554854 Review.
-
Diagnostic and prognostic predictive values of circulating KL-6 for interstitial lung disease: A PRISMA-compliant systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Apr;99(16):e19493. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000019493. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 32311922 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The 'Liaisons dangereuses' Between Lung Cancer and Interstitial Lung Diseases: A Focus on Acute Exacerbation.J Clin Med. 2024 Nov 23;13(23):7085. doi: 10.3390/jcm13237085. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39685543 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chemotherapy for non-small cell lung cancer complicated by idiopathic interstitial pneumonia.Oncol Lett. 2012 Sep;4(3):477-482. doi: 10.3892/ol.2012.753. Epub 2012 Jun 12. Oncol Lett. 2012. PMID: 23741246 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical characteristics and prognostic impact of acute exacerbations in patients with interstitial lung disease and lung cancer: A single-center, retrospective cohort study.Thorac Cancer. 2023 Nov;14(33):3323-3330. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.15124. Epub 2023 Sep 29. Thorac Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37772425 Free PMC article.
-
The role of mucin 1 in respiratory diseases.Eur Respir Rev. 2021 Feb 2;30(159):200149. doi: 10.1183/16000617.0149-2020. Print 2021 Mar 31. Eur Respir Rev. 2021. PMID: 33536260 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical impact of SUVmax of interstitial lesions in lung cancer patients with interstitial lung disease who underwent pulmonary resection.J Thorac Dis. 2022 Oct;14(10):3801-3810. doi: 10.21037/jtd-22-604. J Thorac Dis. 2022. PMID: 36389305 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mizushima Y, Kobayashi M. Clinical characteristics of synchronous multiple lung cancer associated with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. A review of Japanese cases. Chest 1995;108:1272–1277. - PubMed
-
- Aubry MC, Myers JL, Douglas WW, et al. Primary pulmonary carcinoma in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Mayo Clin Proc 2002;77:763–770. - PubMed
-
- Ohyabu N, Hinou H, Matsushita T, et al. An essential epitope of anti‐MUC1 monoclonal antibody KL‐6 revealed by focused glycopeptide library. J Am Chem Soc 2009;131:17102–17109. - PubMed
-
- Oyama T, Kohno N, Yokoyama A, et al. Detection of interstitial pneumonitis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis by measuring circulating levels of KL‐6, a human MUC1 mucin. Lung 1997;175:379–385. - PubMed
-
- Takahashi T, Munakata M, Suzuki I, Kawakami Y. Serum and bronchoalveolar fluid KL‐6 levels in patients with pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1998;158:1294–1298. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

