5-HT₁A receptor binding is increased after recovery from bulimia nervosa compared to control women and is associated with behavioral inhibition in both groups
- PMID: 20872754
- PMCID: PMC4286242
- DOI: 10.1002/eat.20843
5-HT₁A receptor binding is increased after recovery from bulimia nervosa compared to control women and is associated with behavioral inhibition in both groups
Abstract
Objective: Because altered serotonin (5-HT) function appears to persist after recovery from bulimia nervosa (RBN), we investigated the 5-HT(1A) receptor, which could contribute to regulation of appetite, mood, impulse control, or the response to antidepressants.
Method: Thirteen RBN individuals were compared to 21 healthy control women (CW) using positron emission tomography and [carbonyl-(11)C]WAY100635 ([(11)C]WAY).
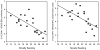
Results: RBN had a 23-34% elevation of [(11)C]WAY binding potential (BP)(P) in subgenual cingulate, mesial temporal, and parietal regions after adjustments for multiple comparisons. For CW, [(11)C]WAY BP(P) was related negatively to novelty seeking, whereas for RBN, [(11)C]WAY BP(P) was related positively to harm avoidance and negatively related to sensation seeking.
Discussion: Alterations of 5-HT(1A) receptor function may provide new insight into efficacy of 5-HT medication in BN, as well as symptoms such as the ability to inhibit or self-control the expression of behaviors related to stimulus seeking, aggression, and impulsivity.
Copyright © 2010 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Serotonin: imaging findings in eating disorders.Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2011;6:59-79. doi: 10.1007/7854_2010_78. Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21243470 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Altered brain serotonin 5-HT1A receptor binding after recovery from anorexia nervosa measured by positron emission tomography and [carbonyl11C]WAY-100635.Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2005 Sep;62(9):1032-41. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.62.9.1032. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2005. PMID: 16143735
-
Altered 5-HT(2A) receptor binding after recovery from bulimia-type anorexia nervosa: relationships to harm avoidance and drive for thinness.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2004 Jun;29(6):1143-55. doi: 10.1038/sj.npp.1300430. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2004. PMID: 15054474 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction between serotonin transporter and dopamine D2/D3 receptor radioligand measures is associated with harm avoidant symptoms in anorexia and bulimia nervosa.Psychiatry Res. 2013 Feb 28;211(2):160-8. doi: 10.1016/j.pscychresns.2012.06.010. Epub 2012 Nov 13. Psychiatry Res. 2013. PMID: 23154100 Free PMC article.
-
Brain imaging of serotonin after recovery from anorexia and bulimia nervosa.Physiol Behav. 2005 Sep 15;86(1-2):15-7. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2005.06.019. Physiol Behav. 2005. PMID: 16102788 Review.
Cited by
-
White matter integrity is reduced in bulimia nervosa.Int J Eat Disord. 2013 Apr;46(3):264-73. doi: 10.1002/eat.22083. Epub 2013 Jan 28. Int J Eat Disord. 2013. PMID: 23354827 Free PMC article.
-
Lack of efficacy of psychological and pharmacological treatments of disorders of eating behavior: neurobiological background.BMC Psychiatry. 2014 Dec 24;14:376. doi: 10.1186/s12888-014-0376-7. BMC Psychiatry. 2014. PMID: 25539757 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Current status of functional imaging in eating disorders.Int J Eat Disord. 2012 Sep;45(6):723-36. doi: 10.1002/eat.22016. Epub 2012 Apr 25. Int J Eat Disord. 2012. PMID: 22532388 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serotonin: imaging findings in eating disorders.Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2011;6:59-79. doi: 10.1007/7854_2010_78. Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21243470 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Perplexities of treatment resistance in eating disorders.BMC Psychiatry. 2013 Nov 7;13:292. doi: 10.1186/1471-244X-13-292. BMC Psychiatry. 2013. PMID: 24199597 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 4. American Psychiatric Association; 2000. Text Revision (DSM-IV-TR)
-
- Kaye W, Fudge J, Paulus M. New insight into symptoms and neurocircuit function of anorexia nervosa. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2009;10:573–584. - PubMed
-
- Rabiner EA, Messa C, Sargent PA, Husted-Kjaer K, Montgomery A, Lawrence AD, et al. A database of [11C]WAY-100635 binding to 5-HT1A receptors in normal male volunteers: Normative data and relationship to methodological, demographic, physiological, and behavioral variables. NeuroImage. 2002;15:620–632. - PubMed
-
- Groenink L, van Bogaert M, van der Gugten J, Oosting R. 5-HT1A receptor and 5-HT1B receptor knockout mice in stress and anxiety paradigms. Behav Pharmacol. 2003;14:369–383. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

