Oncolytic adenovirus SG600-IL24 selectively kills hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines
- PMID: 20872968
- PMCID: PMC2951518
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i37.4677
Oncolytic adenovirus SG600-IL24 selectively kills hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines
Abstract
Aim: To investigate the effect of oncolytic adenovirus SG600-IL24 and replication-incompetent adenovirus Ad.IL-24 on hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cell lines and normal liver cell line.
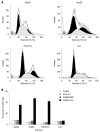
Methods: HCC cell lines (HepG2, Hep3B and MHCC97L) and normal liver cell line (L02) with a different p53 status were infected with SG600-IL24 and Ad.IL-24, respectively. Melanoma differentiation-associated (MDA)-7/interleukin (IL)-24 mRNA and protein expressions in infected cells were detected by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR), enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), and Western blotting, respectively. Apoptosis of HCC cells and normal liver cells was detected by cytometric assay with Hoechst33258 staining. 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay was used to investigate proliferation of HCC cells and normal liver cells, and cell cycle was assayed by flow cytometry.
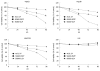
Results: RT-PCR, ELISA and Western blotting showed that the exogenous MDA-7/IL-24 gene was highly expressed in cells infected with SG600-IL24. MTT indicated that SG600-IL24 could suppress the growth of HepG2, Hep3B, MHCC97L, with an inhibition rate of 75% ± 2.5%, 85% ± 2.0%, 72% ± 1.8%, respectively (P < 0.01), promote the apoptosis of HepG2, Hep3B, MHCC97L, with an apoptosis rate of 56.59% ± 4.0%, 78.36% ± 3.5%, 43.39% ± 2.5%, respectively (P < 0.01), and block the HCC cell lines in the G2/M phase with a blocking rate of 35.4% ± 4.2%, 47.3% ± 6.2%, 42% ± 5.0%, respectively (P < 0.01) but not the normal liver cell line in a p53-independent manner.
Conclusion: SG600-IL24 can selectively suppress the proliferation and apoptosis of HCC cell lines in vitro but not normal liver cell line L02 in a p53-independent manner. Compared with Ad.IL-24, SG600-IL24 can significantly enhance the antitumor activity in HCC cell lines.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Interferon-α enhances antitumor activities of oncolytic adenovirus-mediated IL-24 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma.Mol Cancer. 2012 May 8;11:31. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-11-31. Mol Cancer. 2012. PMID: 22569271 Free PMC article.
-
[Adenovirus vector expressing MDA-7/IL-24 selectively induces growth arrests and apoptosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines independent of the state of p53 gene].Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2006 Sep;14(9):670-5. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2006. PMID: 16995981 Chinese.
-
Melanoma differentiation-associated gene-7, MDA-7/IL-24, selectively induces growth suppression, apoptosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma cell line HepG2 by replication-incompetent adenovirus vector.World J Gastroenterol. 2006 Mar 21;12(11):1774-9. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i11.1774. World J Gastroenterol. 2006. PMID: 16586551 Free PMC article.
-
Oncolytic adenovirus-mediated MDA-7/IL-24 overexpression enhances antitumor activity in hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines.Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2010 Dec;9(6):615-21. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2010. PMID: 21134831
-
[Melanoma differentiation associated gene-7 and interleukin-24 selectively induces growth arrest and apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines in vitro].Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2007 Sep 1;45(17):1202-5. Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2007. PMID: 18067718 Chinese.
Cited by
-
Oncolytic Adenovirus-A Nova for Gene-Targeted Oncolytic Viral Therapy in HCC.Front Oncol. 2019 Nov 8;9:1182. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.01182. eCollection 2019. Front Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31781493 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lentivirus‑mediated MDA7/IL24 expression inhibits the proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma cells.Mol Med Rep. 2018 Apr;17(4):5764-5773. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2018.8616. Epub 2018 Feb 16. Mol Med Rep. 2018. PMID: 29484443 Free PMC article.
-
Interferon-α enhances antitumor activities of oncolytic adenovirus-mediated IL-24 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma.Mol Cancer. 2012 May 8;11:31. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-11-31. Mol Cancer. 2012. PMID: 22569271 Free PMC article.
-
Chapter One---Cancer terminator viruses and approaches for enhancing therapeutic outcomes.Adv Cancer Res. 2012;115:1-38. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-398342-8.00001-X. Adv Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 23021240 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Construction of expressing vectors including melanoma differentiation-associated gene-7 (mda-7) fused with the RGD sequences for better tumor targeting.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2015 Aug;18(8):780-7. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2015. PMID: 26557967 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Itamoto T, Nakahara H, Amano H, Kohashi T, Ohdan H, Tashiro H, Asahara T. Repeat hepatectomy for recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma. Surgery. 2007;141:589–597. - PubMed
-
- Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P. Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 2005;55:74–108. - PubMed
-
- Jiang H, Lin JJ, Su ZZ, Goldstein NI, Fisher PB. Subtraction hybridization identifies a novel melanoma differentiation associated gene, mda-7, modulated during human melanoma differentiation, growth and progression. Oncogene. 1995;11:2477–2486. - PubMed
-
- Yacoub A, Hamed HA, Allegood J, Mitchell C, Spiegel S, Lesniak MS, Ogretmen B, Dash R, Sarkar D, Broaddus WC, et al. PERK-dependent regulation of ceramide synthase 6 and thioredoxin play a key role in mda-7/IL-24-induced killing of primary human glioblastoma multiforme cells. Cancer Res. 2010;70:1120–1129. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

