Efficacy trial of a brief cognitive-behavioral depression prevention program for high-risk adolescents: effects at 1- and 2-year follow-up
- PMID: 20873893
- PMCID: PMC3715136
- DOI: 10.1037/a0020544
Efficacy trial of a brief cognitive-behavioral depression prevention program for high-risk adolescents: effects at 1- and 2-year follow-up
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the effects of a brief group cognitive-behavioral (CB) depression prevention program for high-risk adolescents with elevated depressive symptoms at 1- and 2-year follow-up.
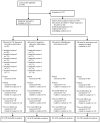
Method: In this indicated prevention trial, 341 at-risk youths were randomized to a group CB intervention, group supportive expressive intervention, CB bibliotherapy, or educational brochure control condition.
Results: Significantly greater reductions in depressive symptoms were shown by group CB participants relative to brochure control participants by 1-year follow-up and bibliotherapy participants by 1- and 2-year follow-up but not relative to supportive expressive participants. Supportive expressive participants showed greater symptom reduction than CB bibliotherapy participants did at 2-year follow-up. Risk for onset of major or minor depression over the 2-year follow-up was significantly lower for group CB participants (14%; odds ratio = 2.2) and CB bibliotherapy participants (3%; odds ratio = 8.1) than for brochure controls (23%).
Conclusions: Results indicate that this group CB intervention reduces initial symptoms and risk for future depressive episodes, although both supportive expressive therapy and CB bibliotherapy also produce intervention effects that persist long term. Indeed, CB bibliotherapy emerged as the least expensive method of reducing risk for future episodes of depression.
(c) 2010 APA, all rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- American Psychological Association Task Force on Psychological Intervention Guidelines. Template for developing guidelines: Interventions for mental disorders and psychological aspects of physical disorders. Washington, DC: APA; 1995.
-
- Burns DD. Feeling Good: The New Mood Therapy. New York: William Morrow & Company; 1980.
-
- Beck AT, Steer RM, Garbin M. Psychometric properties of the Beck Depression Inventory: 25 years of evaluation. Clinical Psychology Review. 1988;8:77–100.
-
- Brent DA, Holder D, Kolko D, Birmaher B, Baugher M, Roth C, Iyengar S, Johnson BA. A clinical psychotherapy trial for adolescent depression comparing cognitive, family, and supportive therapy. Archives of General Psychiatry. 1997;54:877–885. - PubMed
-
- Cantwell DP, Lewinsohn PM, Rohde P, Seeley JR. Correspondence between adolescent report and parent report of psychiatric diagnostic data. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry. 1997;36:610–619. - PubMed