Functional analysis of novel analogues of E3330 that block the redox signaling activity of the multifunctional AP endonuclease/redox signaling enzyme APE1/Ref-1
- PMID: 20874257
- PMCID: PMC3061197
- DOI: 10.1089/ars.2010.3410
Functional analysis of novel analogues of E3330 that block the redox signaling activity of the multifunctional AP endonuclease/redox signaling enzyme APE1/Ref-1
Abstract
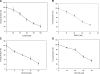
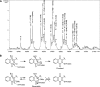
APE1 is a multifunctional protein possessing DNA repair and redox activation of transcription factors. Blocking these functions leads to apoptosis, antiangiogenesis, cell-growth inhibition, and other effects, depending on which function is blocked. Because a selective inhibitor of the APE redox function has potential as a novel anticancer therapeutic, new analogues of E3330 were synthesized. Mass spectrometry was used to characterize the interactions of the analogues (RN8-51, 10-52, and 7-60) with APE1. RN10-52 and RN7-60 were found to react rapidly with APE1, forming covalent adducts, whereas RN8-51 reacted reversibly. Median inhibitory concentration (IC(50) values of all three compounds were significantly lower than that of E3330. EMSA, transactivation assays, and endothelial tube growth-inhibition analysis demonstrated the specificity of E3330 and its analogues in blocking the APE1 redox function and demonstrated that the analogues had up to a sixfold greater effect than did E3330. Studies using cancer cell lines demonstrated that E3330 and one analogue, RN8-51, decreased the cell line growth with little apoptosis, whereas the third, RN7-60, caused a dramatic effect. RN8-51 shows particular promise for further anticancer therapeutic development. This progress in synthesizing and isolating biologically active novel E3330 analogues that effectively inhibit the APE1 redox function validates the utility of further translational anticancer therapeutic development.
Figures








Similar articles
-
NMR studies reveal an unexpected binding site for a redox inhibitor of AP endonuclease 1.Biochemistry. 2011 Dec 6;50(48):10540-9. doi: 10.1021/bi201071g. Epub 2011 Nov 9. Biochemistry. 2011. PMID: 22032234 Free PMC article.
-
Design and synthesis of novel quinone inhibitors targeted to the redox function of apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease 1/redox enhancing factor-1 (Ape1/ref-1).J Med Chem. 2010 Feb 11;53(3):1200-10. doi: 10.1021/jm9014857. J Med Chem. 2010. PMID: 20067291 Free PMC article.
-
Small-molecule inhibitor of the AP endonuclease 1/REF-1 E3330 inhibits pancreatic cancer cell growth and migration.Mol Cancer Ther. 2008 Jul;7(7):2012-21. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-08-0113. Mol Cancer Ther. 2008. PMID: 18645011 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitors of nuclease and redox activity of apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease 1/redox effector factor 1 (APE1/Ref-1).Bioorg Med Chem. 2017 May 1;25(9):2531-2544. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2017.01.028. Epub 2017 Jan 21. Bioorg Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 28161249 Review.
-
APE1/Ref-1 role in redox signaling: translational applications of targeting the redox function of the DNA repair/redox protein APE1/Ref-1.Curr Mol Pharmacol. 2012 Jan;5(1):36-53. doi: 10.2174/1874467211205010036. Curr Mol Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22122463 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The repair function of the multifunctional DNA repair/redox protein APE1 is neuroprotective after ionizing radiation.DNA Repair (Amst). 2011 Sep 5;10(9):942-52. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2011.06.004. Epub 2011 Jul 8. DNA Repair (Amst). 2011. PMID: 21741887 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting APE1/Ref-1 to alleviate formalin-induced pain and spinal neuro-inflammation in rats: a promising therapeutic approach.Front Neurosci. 2025 Jul 30;19:1542264. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2025.1542264. eCollection 2025. Front Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40809401 Free PMC article.
-
Bis-Cinnamamide Derivatives as APE/Ref-1 Inhibitors for the Treatment of Human Melanoma.Molecules. 2022 Apr 21;27(9):2672. doi: 10.3390/molecules27092672. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35566022 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelial cell tumor growth is Ape/ref-1 dependent.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2015 Sep 1;309(5):C296-307. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00022.2015. Epub 2015 Jun 24. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2015. PMID: 26108661 Free PMC article.
-
Apurinic/Apyrimidinic Endonuclease 1/Redox Factor-1 (Ape1/Ref-1) Modulates Antigen Presenting Cell-mediated T Helper Cell Type 1 Responses.J Biol Chem. 2016 Nov 4;291(45):23672-23680. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.742353. Epub 2016 Sep 16. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27637330 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bobola MS. Blank A. Berger MS. Stevens BA. Silber JR. Apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease activity is elevated in human adult gliomas. Clin Cancer Res. 2001;7:3510–3518. - PubMed
-
- Dudley J. Das S. Mukherjee S. Das DK. Resveratrol, a unique phytoalexin present in red wine, delivers either survival signal or death signal to the ischemic myocardium depending on dose. J Nutri Biochem. 2009;20:443–452. - PubMed
-
- Evans AR. Limp-Foster M. Kelley MR. Going APE over ref-1. Mutat Res. 2000;461(2):83–108. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

