Mechanisms of dNTP supply that play an essential role in maintaining genome integrity in eukaryotic cells
- PMID: 20874841
- PMCID: PMC11158391
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2010.01719.x
Mechanisms of dNTP supply that play an essential role in maintaining genome integrity in eukaryotic cells
Abstract
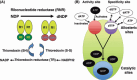
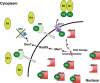
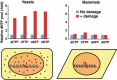
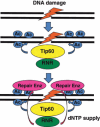
Optimization of intracellular concentrations of dNTPs is critical for the fidelity of DNA synthesis during DNA replication and repair because levels that are too high or too low can easily lead to increased rates of mutagenesis. Recent advances in the analysis of intracellular concentrations of dNTPs have suggested that eukaryotes use diverse mechanisms in supplying dNTPs for DNA synthesis during DNA replication and repair. The enzyme ribonucleotide reductase (RNR) is a key enzyme involved in the synthesis of dNTPs. We found that Tip60-dependent recruitment of RNR at sites of DNA damage is essential for supplying a sufficient amount of dNTPs for mammalian DNA repair. In this review, we focus on recent findings related to RNR regulation in eukaryotes of the dNTPs supplied for DNA synthesis. We also discuss the effect of this regulation on mutagenesis and tumorigenesis.
© 2010 Japanese Cancer Association.
Figures
References
-
- Nordlund P, Reichard P. Ribonucleotide reductases. Annu Rev Biochem 2006; 75: 681–706. - PubMed
-
- Kashlan OB, Scott CP, Lear JD, Cooperman BS. A comprehensive model for the allosteric regulation of mammalian ribonucleotide reductase. Functional consequences of ATP‐ and dATP‐induced oligomerization of the large subunit. Biochemistry 2002; 41: 462–74. - PubMed
-
- Rofougaran R, Vodnala M, Hofer A. Enzymatically active mammalian ribonucleotide reductase exists primarily as an alpha6beta2 octamer. J Biol Chem 2006; 281: 27705–11. - PubMed
-
- Kolberg M, Strand KR, Graff P, Andersson KK. Structure, function, and mechanism of ribonucleotide reductases. Biochim Biophys Acta 2004; 1699: 1–34. - PubMed
-
- Tanaka H, Arakawa H, Yamaguchi T et al. A ribonucleotide reductase gene involved in a p53‐dependent cell‐cycle checkpoint for DNA damage. Nature 2000; 404: 42–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

