Contributions of electron microscopy to understand secretion of immune mediators by human eosinophils
- PMID: 20875166
- PMCID: PMC3420811
- DOI: 10.1017/S1431927610093864
Contributions of electron microscopy to understand secretion of immune mediators by human eosinophils
Abstract
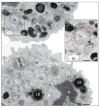
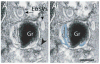
Mechanisms governing secretion of proteins underlie the biologic activities and functions of human eosinophils, leukocytes of the innate immune system, involved in allergic, inflammatory, and immunoregulatory responses. In response to varied stimuli, eosinophils are recruited from the circulation into inflammatory foci, where they modulate immune responses through the release of granule-derived products. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) is the only technique that can clearly identify and distinguish between different modes of cell secretion. In this review, we highlight the advances in understanding mechanisms of eosinophil secretion, based on TEM findings, that have been made over the past years and that have provided unprecedented insights into the functional capabilities of these cells.
Figures


References
-
- Adamko DJ, Odemuyiwa SO, Vethanayagam D, Moqbel R. The rise of the phoenix: The expanding role of the eosinophil in health and disease. Allergy. 2005;60(1):13–22. - PubMed
-
- Ahlstrom-Emanuelsson CA, Greiff L, Andersson M, Persson CG, Erjefalt JS. Eosinophil degranulation status in allergic rhinitis: Observations before and during seasonal allergen exposure. Eur Respir J. 2004;24(5):750–757. - PubMed
-
- Armengot M, Garin L, Carda C. Eosinophil degranulation patterns in nasal polyposis: An ultrastructural study. Am J Rhinol Allergy. 2009;23(5):466–470. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

