Allosteric inhibition of complement function by a staphylococcal immune evasion protein
- PMID: 20876141
- PMCID: PMC2955122
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1003750107
Allosteric inhibition of complement function by a staphylococcal immune evasion protein
Abstract
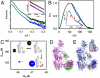
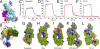
The complement system is a major target of immune evasion by Staphylococcus aureus. Although many evasion proteins have been described, little is known about their molecular mechanisms of action. Here we demonstrate that the extracellular fibrinogen-binding protein (Efb) from S. aureus acts as an allosteric inhibitor by inducing conformational changes in complement fragment C3b that propagate across several domains and influence functional regions far distant from the Efb binding site. Most notably, the inhibitor impaired the interaction of C3b with complement factor B and, consequently, formation of the active C3 convertase. As this enzyme complex is critical for both activation and amplification of the complement response, its allosteric inhibition likely represents a fundamental contribution to the overall immune evasion strategy of S. aureus.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: B.V.G. and J.D.L. are the inventors of a patent application about the use of Efb-C for therapeutic complement inhibition.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 AI081982/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI068730/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- S10 RR029388/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- AI071028/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI071028/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- GM062134/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI030040/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- N01 AI030040/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- NS070899/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- AI076961/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- CA118595/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 CA099835/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- AI081982/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 CA118595/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA099835/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- GM093325/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM093325/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI076961/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI072106/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI2008031/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- RR029388/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM062134/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R33 CA099835/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS070899/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI068730/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI072106/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

