The coordinated increased expression of biliverdin reductase and heme oxygenase-2 promotes cardiomyocyte survival: a reductase-based peptide counters β-adrenergic receptor ligand-mediated cardiac dysfunction
- PMID: 20876213
- PMCID: PMC3005435
- DOI: 10.1096/fj.10-166454
The coordinated increased expression of biliverdin reductase and heme oxygenase-2 promotes cardiomyocyte survival: a reductase-based peptide counters β-adrenergic receptor ligand-mediated cardiac dysfunction
Abstract
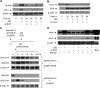
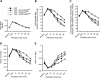
HO-2 oxidizes heme to CO and biliverdin; the latter is reduced to bilirubin by biliverdin reductase (BVR). In addition, HO-2 is a redox-sensitive K/Ca(2)-associated protein, and BVR is an S/T/Y kinase. The two enzymes are components of cellular defense mechanisms. This is the first reporting of regulation of HO-2 by BVR and that their coordinated increase in isolated myocytes and intact heart protects against cardiotoxicity of β-adrenergic receptor activation by isoproterenol (ISO). The induction of BVR mRNA, protein, and activity and HO-2 protein was maintained for ≥ 96 h; increase in HO-1 was modest and transient. In isolated cardiomyocytes, experiments with cycloheximide, proteasome inhibitor MG-132, and siBVR suggested BVR-mediated stabilization of HO-2. In both models, activation of BVR offered protection against the ligand's stimulation of apoptosis. Two human BVR-based peptides known to inhibit and activate the reductase, KKRILHC(281) and KYCCSRK(296), respectively, were tested in the intact heart. Perfusion of the heart with the inhibitory peptide blocked ISO-mediated BVR activation and augmented apoptosis; conversely, perfusion with the activating peptide inhibited apoptosis. At the functional level, peptide-mediated inhibition of BVR was accompanied by dysfunction of the left ventricle and decrease in HO-2 protein levels. Perfusion of the organ with the activating peptide preserved the left ventricular contractile function and was accompanied by increased levels of HO-2 protein. Finding that BVR and HO-2 levels, myocyte apoptosis, and contractile function of the heart can be modulated by small human BVR-based peptides offers a promising therapeutic approach for treatment of cardiac dysfunctions.
Figures


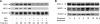


References
-
- Olivetti G., Abbi R., Quaini F., Kajstura J., Cheng W., Nitahara J. A., Quaini E., Di Loreto C., Beltrami C. A., Krajewski S., Reed J. C., Anversa P. (1997) Apoptosis in the failing human heart. N. Engl. J. Med. 336, 1131–1141 - PubMed
-
- Tomita H., Nazmy M., Kajimoto K., Yehia G., Molina C. A., Sadoshima J. (2003) Inducible cAMP early repressor (ICER) is a negative-feedback regulator of cardiac hypertrophy and an important mediator of cardiac myocyte apoptosis in response to beta-adrenergic receptor stimulation. Circ. Res. 93, 12–22 - PubMed
-
- Zaugg M., Xu W., Lucchinetti E., Shafiq S. A., Jamali N. Z., Siddiqui M. A. (2000) Beta-adrenergic receptor subtypes differentially affect apoptosis in adult rat ventricular myocytes. Circulation 102, 344–350 - PubMed
-
- Bristow M. R., Ginsburg R., Umans V., Fowler M., Minobe W., Rasmussen R., Zera P., Menlove R., Shah P., Jamieson S., Stinson E. B. (1986) Beta 1- and beta 2-adrenergic-receptor subpopulations in nonfailing and failing human ventricular myocardium: coupling of both receptor subtypes to muscle contraction and selective beta 1-receptor down-regulation in heart failure. Circ. Res. 59, 297–309 - PubMed
-
- Del Monte F., Kaumann A. J., Poole-Wilson P. A., Wynne D. G., Pepper J., Harding S. E. (1993) Coexistence of functioning beta 1- and beta 2-adrenoceptors in single myocytes from human ventricle. Circulation 88, 854–863 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

