Coa3 and Cox14 are essential for negative feedback regulation of COX1 translation in mitochondria
- PMID: 20876281
- PMCID: PMC2953447
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.201007026
Coa3 and Cox14 are essential for negative feedback regulation of COX1 translation in mitochondria
Abstract
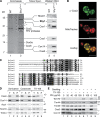
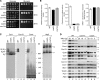
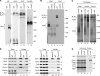
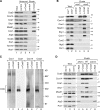
Regulation of eukaryotic cytochrome oxidase assembly occurs at the level of Cox1 translation, its central mitochondria-encoded subunit. Translation of COX1 messenger RNA is coupled to complex assembly in a negative feedback loop: the translational activator Mss51 is thought to be sequestered to assembly intermediates, rendering it incompetent to promote translation. In this study, we identify Coa3 (cytochrome oxidase assembly factor 3; Yjl062w-A), a novel regulator of mitochondrial COX1 translation and cytochrome oxidase assembly. We show that Coa3 and Cox14 form assembly intermediates with newly synthesized Cox1 and are required for Mss51 association with these complexes. Mss51 exists in equilibrium between a latent, translational resting, and a committed, translation-effective, state that are represented as distinct complexes. Coa3 and Cox14 promote formation of the latent state and thus down-regulate COX1 expression. Consequently, lack of Coa3 or Cox14 function traps Mss51 in the committed state and promotes Cox1 synthesis. Our data indicate that Coa1 binding to sequestered Mss51 in complex with Cox14, Coa3, and Cox1 is essential for full inactivation.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

