The p400 ATPase regulates nucleosome stability and chromatin ubiquitination during DNA repair
- PMID: 20876283
- PMCID: PMC2953432
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.201001160
The p400 ATPase regulates nucleosome stability and chromatin ubiquitination during DNA repair
Abstract
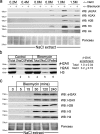
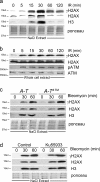
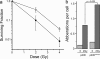
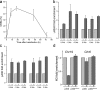
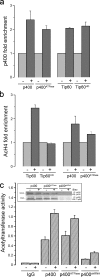
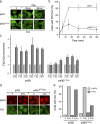
The complexity of chromatin architecture presents a significant barrier to the ability of the DNA repair machinery to access and repair DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs). Consequently, remodeling of the chromatin landscape adjacent to DSBs is vital for efficient DNA repair. Here, we demonstrate that DNA damage destabilizes nucleosomes within chromatin regions that correspond to the γ-H2AX domains surrounding DSBs. This nucleosome destabilization is an active process requiring the ATPase activity of the p400 SWI/SNF ATPase and histone acetylation by the Tip60 acetyltransferase. p400 is recruited to DSBs by a mechanism that is independent of ATM but requires mdc1. Further, the destabilization of nucleosomes by p400 is required for the RNF8-dependent ubiquitination of chromatin, and for the subsequent recruitment of brca1 and 53BP1 to DSBs. These results identify p400 as a novel DNA damage response protein and demonstrate that p400-mediated alterations in nucleosome and chromatin structure promote both chromatin ubiquitination and the accumulation of brca1 and 53BP1 at sites of DNA damage.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Chromatin dynamics and the repair of DNA double strand breaks.Cell Cycle. 2011 Jan 15;10(2):261-7. doi: 10.4161/cc.10.2.14543. Epub 2011 Jan 15. Cell Cycle. 2011. PMID: 21212734 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Histone H2A.Z controls a critical chromatin remodeling step required for DNA double-strand break repair.Mol Cell. 2012 Dec 14;48(5):723-33. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2012.09.026. Epub 2012 Oct 30. Mol Cell. 2012. PMID: 23122415 Free PMC article.
-
Ataxia telangiectasia mutated (ATM) interacts with p400 ATPase for an efficient DNA damage response.BMC Mol Biol. 2016 Nov 4;17(1):22. doi: 10.1186/s12867-016-0075-7. BMC Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 27814680 Free PMC article.
-
Crosstalk between histone modifications during the DNA damage response.Trends Cell Biol. 2009 May;19(5):207-17. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2009.03.001. Epub 2009 Apr 1. Trends Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19342239 Review.
-
The chromatin remodeler p400 ATPase facilitates Rad51-mediated repair of DNA double-strand breaks.J Cell Biol. 2012 Dec 24;199(7):1067-81. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201205059. J Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 23266955 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Eaf1 Links the NuA4 Histone Acetyltransferase Complex to Htz1 Incorporation and Regulation of Purine Biosynthesis.Eukaryot Cell. 2015 Jun;14(6):535-44. doi: 10.1128/EC.00004-15. Epub 2015 Apr 3. Eukaryot Cell. 2015. PMID: 25841019 Free PMC article.
-
HJURP is recruited to double-strand break sites and facilitates DNA repair by promoting chromatin reorganization.Oncogene. 2024 Mar;43(11):804-820. doi: 10.1038/s41388-024-02937-1. Epub 2024 Jan 26. Oncogene. 2024. PMID: 38279062
-
JMJD6 modulates DNA damage response through downregulating H4K16ac independently of its enzymatic activity.Cell Death Differ. 2020 Mar;27(3):1052-1066. doi: 10.1038/s41418-019-0397-3. Epub 2019 Jul 29. Cell Death Differ. 2020. PMID: 31358914 Free PMC article.
-
Chromatin Ubiquitination Guides DNA Double Strand Break Signaling and Repair.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Jul 5;10:928113. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.928113. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35865631 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling complexes as novel targets for cancer therapy.Adv Cancer Res. 2014;121:183-233. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-800249-0.00005-6. Adv Cancer Res. 2014. PMID: 24889532 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

