Why Dom34 stimulates growth of cells with defects of 40S ribosomal subunit biosynthesis
- PMID: 20876302
- PMCID: PMC2976434
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00618-10
Why Dom34 stimulates growth of cells with defects of 40S ribosomal subunit biosynthesis
Abstract
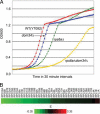
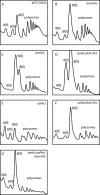
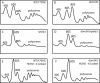
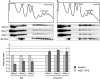
A set of genome-wide screens for proteins whose absence exacerbates growth defects due to pseudo-haploinsufficiency of ribosomal proteins in Saccharomyces cerevisiae identified Dom34 as being particularly important for cell growth when there is a deficit of 40S ribosomal subunits. In contrast, strains with a deficit of 60S ribosomal proteins were largely insensitive to the loss of Dom34. The slow growth of cells lacking Dom34 and haploinsufficient for a protein of the 40S subunit is caused by a severe shortage of 40S subunits available for translation initiation due to a combination of three effects: (i) the natural deficiency of 40S subunits due to defective synthesis, (ii) the sequestration of 40S subunits due to the large accumulation of free 60S subunits, and (iii) the accumulation of ribosomes "stuck" in a distinct 80S form, insensitive to the Mg(2+) concentration, and at least temporarily unavailable for further translation. Our data suggest that these stuck ribosomes have neither mRNA nor tRNA. We postulate, based on our results and on previously published work, that the stuck ribosomes arise because of the lack of Dom34, which normally resolves a ribosome stalled due to insufficient tRNAs, to structural problems with its mRNA, or to a defect in the ribosome itself.
Figures


References
-
- Costanzo, M., A. Baryshnikova, J. Bellay, Y. Kim, E. D. Spear, C. S. Sevier, H. Ding, J. L. Koh, K. Toufighi, S. Mostafavi, J. Prinz, R. P. St. Onge, B. VanderSluis, T. Makhnevych, F. J. Vizeacoumar, S. Alizadeh, S. Bahr, R. L. Brost, Y. Chen, M. Cokol, R. Deshpande, Z. Li, Z. Y. Lin, W. Liang, M. Marback, J. Paw, B. J. San Luis, E. Shuteriqi, A. H. Tong, N. van Dyke, I. M. Wallace, J. A. Whitney, M. T. Weirauch, G. Zhong, H. Zhu, W. A. Houry, M. Brudno, S. Ragibizadeh, B. Papp, C. Pal, F. P. Roth, G. Giaever, C. Nislow, O. G. Troyanskaya, H. Bussey, G. D. Bader, A. C. Gingras, Q. D. Morris, P. M. Kim, C. A. Kaiser, C. L. Myers, B. J. Andrews, and C. Boone. 2010. The genetic landscape of a cell. Science 327:425-431. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
