Age-dependent susceptibility to a viral disease due to decreased natural killer cell numbers and trafficking
- PMID: 20876312
- PMCID: PMC2964566
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20100282
Age-dependent susceptibility to a viral disease due to decreased natural killer cell numbers and trafficking
Abstract
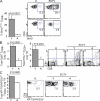
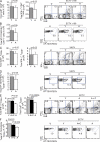
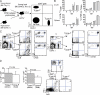
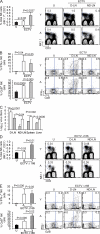
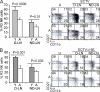
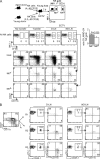
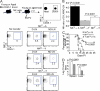
Although it is well known that aged hosts are generally more susceptible to viral diseases than the young, specific dysfunctions of the immune system directly responsible for this increased susceptibility have yet to be identified. We show that mice genetically resistant to mousepox (the mouse parallel of human smallpox) lose resistance at mid-age. Surprisingly, this loss of resistance is not a result of intrinsically defective T cell responses. Instead, the primary reason for the loss of resistance results from a decreased number of total and mature natural killer (NK) cells in the blood and an intrinsic impairment in their ability to migrate to the lymph node draining the site of infection, which is essential to curb systemic virus spread. Hence, our work links the age-dependent increase in susceptibility to a viral disease to a specific defect of NK cells, opening the possibility of exploring treatments to improve NK cell function in the aged with the goal of enhancing their resistance to viral diseases.
Figures
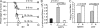

Similar articles
-
Chronic Lymphocytic Choriomeningitis Infection Causes Susceptibility to Mousepox and Impairs Natural Killer Cell Maturation and Function.J Virol. 2020 Feb 14;94(5):e01831-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01831-19. Print 2020 Feb 14. J Virol. 2020. PMID: 31776282 Free PMC article.
-
Studying NK cell responses to ectromelia virus infections in mice.Methods Mol Biol. 2010;612:411-28. doi: 10.1007/978-1-60761-362-6_28. Methods Mol Biol. 2010. PMID: 20033657
-
Deficiency in Th2 cytokine responses exacerbate orthopoxvirus infection.PLoS One. 2015 Mar 9;10(3):e0118685. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0118685. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25751266 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic resistance to smallpox: lessons from mousepox.Novartis Found Symp. 2007;281:129-36; discussion 136-40, 208-9. doi: 10.1002/9780470062128.ch11. Novartis Found Symp. 2007. PMID: 17534070 Review.
-
The Pathogenesis and Immunobiology of Mousepox.Adv Immunol. 2016;129:251-76. doi: 10.1016/bs.ai.2015.10.001. Epub 2015 Nov 21. Adv Immunol. 2016. PMID: 26791861 Review.
Cited by
-
Crosstalk between the type 1 interferon and nuclear factor kappa B pathways confers resistance to a lethal virus infection.Cell Host Microbe. 2013 Jun 12;13(6):701-10. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2013.04.015. Cell Host Microbe. 2013. PMID: 23768494 Free PMC article.
-
The ectromelia virus SPI-2 protein causes lethal mousepox by preventing NK cell responses.J Virol. 2011 Nov;85(21):11170-82. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00256-11. Epub 2011 Aug 17. J Virol. 2011. PMID: 21849445 Free PMC article.
-
Natural killer cells as participants in pathogenesis of rat experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE): lessons from research on rats with distinct age and strain.Cent Eur J Immunol. 2019;44(4):337-356. doi: 10.5114/ceji.2019.92777. Epub 2020 Jan 20. Cent Eur J Immunol. 2019. PMID: 32140045 Free PMC article.
-
Viral Infection and Dissemination Through the Lymphatic System.Microorganisms. 2025 Feb 18;13(2):443. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms13020443. Microorganisms. 2025. PMID: 40005808 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Is there a sicker sex? Dose relationships modify male-female differences in infection prevalence.Proc Biol Sci. 2024 Jan 10;291(2014):20232575. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2023.2575. Epub 2024 Jan 10. Proc Biol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38196362 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Basta S., Chen W., Bennink J.R., Yewdell J.W. 2002. Inhibitory effects of cytomegalovirus proteins US2 and US11 point to contributions from direct priming and cross-priming in induction of vaccinia virus-specific CD8(+) T cells. J. Immunol. 168:5403–5408 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

