Activation of the K(ATP) channel by Mg-nucleotide interaction with SUR1
- PMID: 20876358
- PMCID: PMC2947056
- DOI: 10.1085/jgp.201010475
Activation of the K(ATP) channel by Mg-nucleotide interaction with SUR1
Abstract
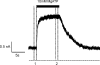
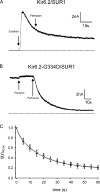
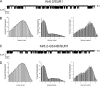
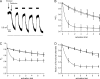
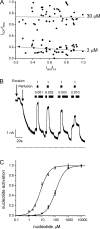
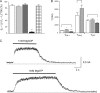
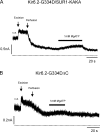
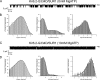
The mechanism of adenosine triphosphate (ATP)-sensitive potassium (K(ATP)) channel activation by Mg-nucleotides was studied using a mutation (G334D) in the Kir6.2 subunit of the channel that renders K(ATP) channels insensitive to nucleotide inhibition and has no apparent effect on their gating. K(ATP) channels carrying this mutation (Kir6.2-G334D/SUR1 channels) were activated by MgATP and MgADP with an EC(50) of 112 and 8 µM, respectively. This activation was largely suppressed by mutation of the Walker A lysines in the nucleotide-binding domains of SUR1: the remaining small (∼10%), slowly developing component of MgATP activation was fully inhibited by the lipid kinase inhibitor LY294002. The EC(50) for activation of Kir6.2-G334D/SUR1 currents by MgADP was lower than that for MgATP, and the time course of activation was faster. The poorly hydrolyzable analogue MgATPγS also activated Kir6.2-G334D/SUR1. AMPPCP both failed to activate Kir6.2-G334D/SUR1 and to prevent its activation by MgATP. Maximal stimulatory concentrations of MgATP (10 mM) and MgADP (1 mM) exerted identical effects on the single-channel kinetics: they dramatically elevated the open probability (P(O) > 0.8), increased the mean open time and the mean burst duration, reduced the frequency and number of interburst closed states, and eliminated the short burst states. By comparing our results with those obtained for wild-type K(ATP) channels, we conclude that the MgADP sensitivity of the wild-type K(ATP) channel can be described quantitatively by a combination of inhibition at Kir6.2 (measured for wild-type channels in the absence of Mg(2+)) and activation via SUR1 (determined for Kir6.2-G334D/SUR1 channels). However, this is not the case for the effects of MgATP.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Kir6.2-F333I mutation differentially modulates KATP channels composed of SUR1 or SUR2 subunits.J Physiol. 2007 Jun 15;581(Pt 3):1259-69. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2007.130211. Epub 2007 Mar 29. J Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17395632 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the C-terminus of SUR in the differential regulation of β-cell and cardiac KATP channels by MgADP and metabolism.J Physiol. 2018 Dec;596(24):6205-6217. doi: 10.1113/JP276708. Epub 2018 Oct 14. J Physiol. 2018. PMID: 30179258 Free PMC article.
-
A mutation in the ATP-binding site of the Kir6.2 subunit of the KATP channel alters coupling with the SUR2A subunit.J Physiol. 2007 Nov 1;584(Pt 3):743-53. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2007.143149. Epub 2007 Sep 13. J Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17855752 Free PMC article.
-
Review. SUR1: a unique ATP-binding cassette protein that functions as an ion channel regulator.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2009 Jan 27;364(1514):257-67. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2008.0142. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2009. PMID: 18990670 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cardiac sarcolemmal K(ATP) channels: Latest twists in a questing tale!J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2010 Jan;48(1):71-5. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2009.07.002. Epub 2009 Jul 14. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2010. PMID: 19607836 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Ligand binding and conformational changes of SUR1 subunit in pancreatic ATP-sensitive potassium channels.Protein Cell. 2018 Jun;9(6):553-567. doi: 10.1007/s13238-018-0530-y. Epub 2018 Mar 28. Protein Cell. 2018. PMID: 29594720 Free PMC article.
-
The Nucleotide-Binding Sites of SUR1: A Mechanistic Model.Biophys J. 2015 Dec 15;109(12):2452-2460. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2015.10.026. Biophys J. 2015. PMID: 26682803 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolic fate of glucose and candidate signaling and excess-fuel detoxification pathways in pancreatic β-cells.J Biol Chem. 2017 May 5;292(18):7407-7422. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.763060. Epub 2017 Mar 9. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28280244 Free PMC article.
-
Calcium dynamics control K-ATP channel-mediated bursting in substantia nigra dopamine neurons: a combined experimental and modeling study.J Neurophysiol. 2018 Jan 1;119(1):84-95. doi: 10.1152/jn.00351.2017. Epub 2017 Oct 4. J Neurophysiol. 2018. PMID: 28978764 Free PMC article.
-
Sulfonylureas suppress the stimulatory action of Mg-nucleotides on Kir6.2/SUR1 but not Kir6.2/SUR2A KATP channels: a mechanistic study.J Gen Physiol. 2014 Nov;144(5):469-86. doi: 10.1085/jgp.201411222. J Gen Physiol. 2014. PMID: 25348414 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abraham M.R., Selivanov V.A., Hodgson D.M., Pucar D., Zingman L.V., Wieringa B., Dzeja P.P., Alekseev A.E., Terzic A. 2002. Coupling of cell energetics with membrane metabolic sensing. Integrative signaling through creatine kinase phosphotransfer disrupted by M-CK gene knock-out. J. Biol. Chem. 277:24427–24434 10.1074/jbc.M201777200 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

