Total raltegravir concentrations in cerebrospinal fluid exceed the 50-percent inhibitory concentration for wild-type HIV-1
- PMID: 20876368
- PMCID: PMC2981289
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.00507-10
Total raltegravir concentrations in cerebrospinal fluid exceed the 50-percent inhibitory concentration for wild-type HIV-1
Abstract
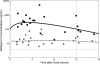
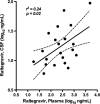
HIV-associated neurocognitive disorders continue to be common. Antiretrovirals that achieve higher concentrations in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) are associated with better control of HIV and improved cognition. The objective of this study was to measure total raltegravir (RAL) concentrations in CSF and to compare them with matched concentrations in plasma and in vitro inhibitory concentrations. Eighteen subjects with HIV-1 infection were enrolled based on the use of RAL-containing regimens and the availability of CSF and matched plasma samples. RAL was measured in 21 CSF and plasma pairs by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry, and HIV RNA was detected by reverse transcription-PCR (RT-PCR). RAL concentrations were compared to the 50% inhibitory concentration (IC(50)) for wild-type HIV-1 (3.2 ng/ml). Volunteers were predominantly middle-aged white men with AIDS and without hepatitis C virus (HCV) coinfection. The median concurrent CD4(+) cell count was 276/μl, and 28% of CD4(+) cell counts were below 200/μl. HIV RNA was detectable in 38% of plasma specimens and 4% of CSF specimens. RAL was present in all CSF specimens, with a median total concentration of 14.5 ng/ml. The median concentration in plasma was 260.9 ng/ml, with a median CSF-to-plasma ratio of 0.058. Concentrations in CSF correlated with those in with plasma (r(2), 0.24; P, 0.02) but not with the postdose sampling time (P, >0.50). RAL concentrations in CSF exceeded the IC(50) for wild-type HIV in all specimens by a median of 4.5-fold. RAL is present in CSF and reaches sufficiently high concentrations to inhibit wild-type HIV in all individuals. As a component of effective antiretroviral regimens or as the main antiretroviral, RAL likely contributes to the control of HIV replication in the nervous system.
Figures
References
-
- Adam, P., O. Sobek, L. Táborský, T. Hildebrand, O. Tutterová, and P. Zácek. 2003. CSF and serum orosomucoid (alpha-1-acid glycoprotein) in patients with multiple sclerosis: a comparison among particular subgroups of MS patients. Clin. Chim. Acta 334:107-110. - PubMed
-
- Capparelli, E. V., D. Holland, C. Okamoto, B. Gragg, J. Durelle, J. Marquie-Beck, G. van den Brande, R. Ellis, and S. Letendre; the HNRC Group. 2005. Lopinavir concentrations in cerebrospinal fluid exceed the 50% inhibitory concentration for HIV. AIDS 19:949-952. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

