MS quality of life, depression, and fatigue improve after mindfulness training: a randomized trial
- PMID: 20876468
- PMCID: PMC3463050
- DOI: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181f4d80d
MS quality of life, depression, and fatigue improve after mindfulness training: a randomized trial
Abstract
Objective: Health-related quality of life (HRQOL) is often much reduced among individuals with multiple sclerosis (MS), and incidences of depression, fatigue, and anxiety are high. We examined effects of a mindfulness-based intervention (MBI) compared to usual care (UC) upon HRQOL, depression, and fatigue among adults with relapsing-remitting or secondary progressive MS.
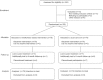
Methods: A total of 150 patients were randomly assigned to the intervention (n = 76) or to UC (n = 74). MBI consisted of a structured 8-week program of mindfulness training. Assessments were made at baseline, postintervention, and 6 months follow-up. Primary outcomes included disease-specific and disease-aspecific HRQOL, depression, and fatigue. Anxiety, personal goal attainment, and adherence to homework were secondary outcomes.
Results: Attrition was low in the intervention group (5%) and attendance rate high (92%). Employing intention-to-treat analysis, MBI, compared with UC, improved nonphysical dimensions of primary outcomes at postintervention and follow-up (p < 0.002); effect sizes, 0.4-0.9 posttreatment and 0.3-0.5 at follow-up. When analyses were repeated among subgroups with clinically relevant levels of preintervention depression, fatigue, or anxiety, postintervention and follow-up effects remained significant and effect sizes were larger than for the total sample.
Conclusions: In addition to evidence of improved HRQOL and well-being, these findings demonstrate broad feasibility and acceptance of, as well as satisfaction and adherence with, a program of mindfulness training for patients with MS. The results may also have treatment implications for other chronic disorders that diminish HRQOL.
Classification of evidence: This trial provides Class III evidence that MBI compared with UC improved HRQOL, fatigue, and depression up to 6 months postintervention.
Figures

Comment in
-
Healing the mind: meditation and multiple sclerosis.Neurology. 2010 Sep 28;75(13):1130-1. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181f4d8ab. Neurology. 2010. PMID: 20876465 No abstract available.
References
-
- Compston A, Confavreux C. The distribution of multiple sclerosis. In: Compston A, ed. McAlpine's Multiple Sclerosis, 4th ed. London: Churchill Livingstone Elsevier; 2005:71–112.
-
- Foley JF, Brandes DW. Redefining functionality and treatment efficacy in multiple sclerosis. Neurology 2009;72:S1–S11. - PubMed
-
- Feinstein A, O'Connor P, Gray T, Feinstein K. The effects of anxiety on psychiatric morbidity in patients with multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler 1999;5:323–326. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
