Proinflammatory signals and the loss of lymphatic vessel hyaluronan receptor-1 (LYVE-1) in the early pathogenesis of laminin alpha2-deficient skeletal muscle
- PMID: 20876525
- PMCID: PMC3201133
- DOI: 10.1369/jhc.2010.956672
Proinflammatory signals and the loss of lymphatic vessel hyaluronan receptor-1 (LYVE-1) in the early pathogenesis of laminin alpha2-deficient skeletal muscle
Abstract
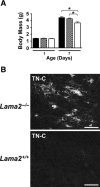
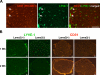
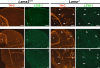
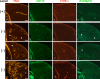
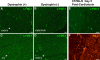
Congenital muscular dystrophy type 1A, a severe neuromuscular disease characterized by early-onset muscle weakness and degeneration, is caused by insufficient levels of laminin α2 (LAMA2) in the basal lamina surrounding muscle fibers and other cells. A better understanding of the molecular mechanisms leading to muscle loss is needed to develop therapeutic interventions for this disease. Here, the authors show that inflammation is an early feature of pathogenesis in Lama2-deficient mouse muscle, indicated by elevated expression of tenascin C in the endomysium around muscle fibers, infiltration of macrophages, and induction of the inflammatory cytokines tumor necrosis factor α (TNFα) and IL-1β. In addition, the expression of lymphatic vessel endothelial hyaluronan receptor-1 (LYVE-1), a specific marker for lymphatic vessel endothelial cells, is dramatically reduced early in Lama2-deficient muscle pathogenesis. LYVE-1 expression, which is inhibited by TNFα, is also decreased in muscles undergoing degeneration due to dystrophin deficiency and cardiotoxin damage. LYVE-1 expression thus provides a useful biomarker to monitor the onset of muscle pathogenesis, likely serving as an indicator of inflammatory signals present in muscles. Together, the data show that inflammatory pathways are activated in the earliest stages of Lama2-deficient disease progression and could play a role in early muscle degeneration.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the authorship and/or publication of this article.
Figures
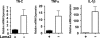
Similar articles
-
Diseased muscles that lack dystrophin or laminin-alpha2 have altered compositions and proliferation of mononuclear cell populations.BMC Neurol. 2005 Apr 7;5(1):7. doi: 10.1186/1471-2377-5-7. BMC Neurol. 2005. PMID: 15817132 Free PMC article.
-
Ku70 regulates Bax-mediated pathogenesis in laminin-alpha2-deficient human muscle cells and mouse models of congenital muscular dystrophy.Hum Mol Genet. 2009 Dec 1;18(23):4467-77. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddp399. Epub 2009 Aug 19. Hum Mol Genet. 2009. PMID: 19692349 Free PMC article.
-
Muscle-specific BCL2 expression ameliorates muscle disease in laminin {alpha}2-deficient, but not in dystrophin-deficient, mice.Hum Mol Genet. 2005 Apr 15;14(8):1029-40. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddi095. Epub 2005 Mar 9. Hum Mol Genet. 2005. PMID: 15757977
-
Laminin-deficient muscular dystrophy: Molecular pathogenesis and structural repair strategies.Matrix Biol. 2018 Oct;71-72:174-187. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2017.11.009. Epub 2017 Nov 27. Matrix Biol. 2018. PMID: 29191403 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Merosin (laminin-2) localization in basal lamina of normal skeletal muscle fibers and changes in plasma membrane of merosin-deficient skeletal muscle fibers.Med Electron Microsc. 2003 Dec;36(4):213-20. doi: 10.1007/s00795-003-0227-y. Med Electron Microsc. 2003. PMID: 16228654 Review.
Cited by
-
A Family of Laminin α2 Chain-Deficient Mouse Mutants: Advancing the Research on LAMA2-CMD.Front Mol Neurosci. 2020 Apr 21;13:59. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2020.00059. eCollection 2020. Front Mol Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32457577 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunobiology of Inherited Muscular Dystrophies.Compr Physiol. 2018 Sep 14;8(4):1313-1356. doi: 10.1002/cphy.c170052. Compr Physiol. 2018. PMID: 30215857 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lymphatic dysfunction correlates with inflammation in a mouse model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.Dis Model Mech. 2025 Jul 1;18(7):dmm052148. doi: 10.1242/dmm.052148. Epub 2025 Jul 16. Dis Model Mech. 2025. PMID: 40600271 Free PMC article.
-
Skeletal Muscle Regeneration in Cardiotoxin-Induced Muscle Injury Models.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 2;23(21):13380. doi: 10.3390/ijms232113380. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36362166 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dysregulation of matricellular proteins is an early signature of pathology in laminin-deficient muscular dystrophy.Skelet Muscle. 2014 Jul 2;4:14. doi: 10.1186/2044-5040-4-14. eCollection 2014. Skelet Muscle. 2014. PMID: 25075272 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arimoto J, Ikura Y, Suekane T, Nakagawa M, Kitabayashi C, Iwasa Y, Sugioka K, Naruko T, Arakawa T, Ueda M. 2010. Expression of LYVE-1 in sinusoidal endothelium is reduced in chronically inflamed human livers. J Gastroenterol. 45(3):317-325 - PubMed
-
- Bentzinger CF, Barzaghi P, Lin S, Ruegg MA. 2005. Overexpression of mini-agrin in skeletal muscle increases muscle integrity and regenerative capacity in laminin-alpha2-deficient mice. FASEB J. 19:934-942 - PubMed
-
- Bushby K, Lochmuller H, Lynn S, Straub V. 2009. Interventions for muscular dystrophy: molecular medicines entering the clinic. Lancet. 374:1849-1856 - PubMed
-
- Chiquet-Ehrismann R, Chiquet M. 2003. Tenascins: regulation and putative functions during pathological stress. J Pathol. 200:488-499 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

