InsP3R-associated cGMP kinase substrate determines inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor susceptibility to phosphoregulation by cyclic nucleotide-dependent kinases
- PMID: 20876535
- PMCID: PMC2988395
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.168989
InsP3R-associated cGMP kinase substrate determines inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor susceptibility to phosphoregulation by cyclic nucleotide-dependent kinases
Abstract
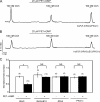
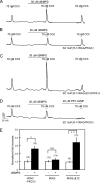
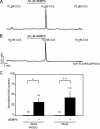
Ca(2+) release through inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptors (InsP(3)R) can be modulated by numerous factors, including input from other signal transduction cascades. These events shape the spatio-temporal characteristics of the Ca(2+) signal and provide fidelity essential for the appropriate activation of effectors. In this study, we investigate the regulation of Ca(2+) release via InsP(3)R following activation of cyclic nucleotide-dependent kinases in the presence and absence of expression of a binding partner InsP(3)R-associated cGMP kinase substrate (IRAG). cGMP-dependent kinase (PKG) phosphorylation of only the S2+ InsP(3)R-1 subtype resulted in enhanced Ca(2+) release in the absence of IRAG expression. In contrast, IRAG bound to each InsP(3)R subtype, and phosphorylation of IRAG by PKG attenuated Ca(2+) release through all InsP(3)R subtypes. Surprisingly, simply the expression of IRAG attenuated phosphorylation and inhibited the enhanced Ca(2+) release through InsP(3)R-1 following cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA) activation. In contrast, IRAG expression did not influence the PKA-enhanced activity of the InsP(3)R-2. Phosphorylation of IRAG resulted in reduced Ca(2+) release through all InsP(3)R subtypes during concurrent activation of PKA and PKG, indicating that IRAG modulation is dominant under these conditions. These studies yield mechanistic insight into how cells with various complements of proteins integrate and prioritize signals from ubiquitous signaling pathways.
Figures






References
-
- Berridge M. J., Bootman M. D., Roderick H. L. (2003) Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 4, 517–529 - PubMed
-
- Patterson R. L., Boehning D., Snyder S. H. (2004) Annu. Rev. Biochem. 73, 437–465 - PubMed
-
- Conti M., Beavo J. (2007) Annu. Rev. Biochem. 76, 481–511 - PubMed
-
- Willoughby D., Cooper D. M. (2007) Physiol. Rev. 87, 965–1010 - PubMed
-
- Berridge M. J., Lipp P., Bootman M. D. (2000) Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 1, 11–21 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

