The Flamingo ortholog FMI-1 controls pioneer-dependent navigation of follower axons in C. elegans
- PMID: 20876647
- PMCID: PMC2959053
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.054320
The Flamingo ortholog FMI-1 controls pioneer-dependent navigation of follower axons in C. elegans
Abstract
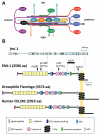
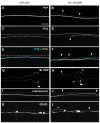
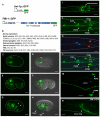
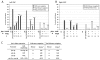
Development of a functional neuronal network during embryogenesis begins with pioneer axons creating a scaffold along which later-outgrowing axons extend. The molecular mechanism used by these follower axons to navigate along pre-existing axons remains poorly understood. We isolated loss-of-function alleles of fmi-1, which caused strong axon navigation defects of pioneer and follower axons in the ventral nerve cord (VNC) of C. elegans. Notably follower axons, which exclusively depend on pioneer axons for correct navigation, frequently separated from the pioneer. fmi-1 is the sole C. elegans ortholog of Drosophila flamingo and vertebrate Celsr genes, and this phenotype defines a new role for this important molecule in follower axon navigation. FMI-1 has a unique and strikingly conserved structure with cadherin and C-terminal G-protein coupled receptor domains and could mediate cell-cell adhesion and signaling functions. We found that follower axon navigation depended on the extracellular but not on the intracellular domain, suggesting that FMI-1 mediates primarily adhesion between pioneer and follower axons. By contrast, pioneer axon navigation required the intracellular domain, suggesting that FMI-1 acts as receptor transducing a signal in this case. Our findings indicate that FMI-1 is a cell-type dependent axon guidance factor with different domain requirements for its different functions in pioneers and followers.
Figures


References
-
- Asakura T., Ogura K., Goshima Y. (2007). UNC-6 expression by the vulval precursor cells of Caenorhabditis elegans is required for the complex axon guidance of the HSN neurons. Dev. Biol. 304, 800-810 - PubMed
-
- Boulin T., Pocock R., Hobert O. (2006). A novel Eph receptor-interacting IgSF protein provides C. elegans motoneurons with midline guidepost function. Curr. Biol. 16, 1871-1883 - PubMed
-
- Broadbent I. D., Pettitt J. (2002). The C. elegans hmr-1 gene can encode a neuronal classic cadherin involved in the regulation of axon fasciculation. Curr. Biol. 12, 59-63 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

