Both polymorphic variable number of tandem repeats and autoimmune regulator modulate differential expression of insulin in human thymic epithelial cells
- PMID: 20876716
- PMCID: PMC3012191
- DOI: 10.2337/db10-0255
Both polymorphic variable number of tandem repeats and autoimmune regulator modulate differential expression of insulin in human thymic epithelial cells
Abstract
Objective: Polymorphic INS-VNTR plays an important role in regulating insulin transcript expression in the human thymus that leads to either insulin autoimmunity or tolerance. The molecular mechanisms underlying the INS-VNTR haplotype-dependent insulin expression are still unclear. In this study, we determined the mechanistic components underlying the differential insulin gene expression in human thymic epithelial cells, which should have profound effects on the insulin autoimmune tolerance induction.
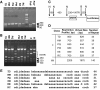
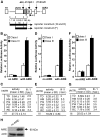
Research design and methods: A repetitive DNA region designated as a variable number of tandem repeats (VNTR) is located upstream of the human insulin gene and correlates with the incidence of type 1 diabetes. We generated six class I and two class III VNTR constructs linked to the human insulin basal promoter or SV40 heterologous promoter/enhancer and demonstrated that AIRE protein modulates the insulin promoter activities differentially through binding to the VNTR region.
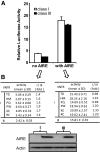
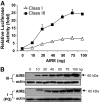
Results: Here we show that in the presence of the autoimmune regulator (AIRE), the class III VNTR haplotype is responsible for an average of three-fold higher insulin expression than class I VNTR in thymic epithelial cells. In a protein-DNA pull-down experiment, AIRE protein is capable of binding to VNTR class I and III probes. Further, the transcriptional activation of the INS-VNTR by AIRE requires the insulin basal promoter. The VNTR sequence loses its activation activity when linked to a heterologous promoter and/or enhancer.
Conclusions: These findings demonstrate a type 1 diabetes predisposition encoded by the INS-VNTR locus and a critical function played by AIRE, which constitute a dual control mechanisms regulating quantitative expression of insulin in human thymic epithelial cells.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Functional Domains of Autoimmune Regulator (AIRE) Modulate INS-VNTR Transcription in Human Thymic Epithelial Cells.J Biol Chem. 2016 May 20;291(21):11313-22. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.722488. Epub 2016 Apr 5. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27048654 Free PMC article.
-
Class III alleles of the variable number of tandem repeat insulin polymorphism associated with silencing of thymic insulin predispose to type 1 diabetes.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2001 Aug;86(8):3705-10. doi: 10.1210/jcem.86.8.7733. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2001. PMID: 11502799
-
Yeast one-hybrid screen of a thymus epithelial library identifies ZBTB7A as a regulator of thymic insulin expression.Mol Immunol. 2013 Dec;56(4):637-42. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2013.05.238. Epub 2013 Aug 1. Mol Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23911422 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of genetic susceptibility to type I diabetes: beyond HLA.Mol Genet Metab. 2004 Mar;81(3):187-95. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2003.11.010. Mol Genet Metab. 2004. PMID: 14972324 Review.
-
[IDDM and variable number of tandem repeats (VNTR) in the 5'region of the insulin gene: a review].Nihon Rinsho. 1997 Oct;55 Suppl:376-81. Nihon Rinsho. 1997. PMID: 9392134 Review. Japanese. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
The position of single-base deletions in the VNTR sequence of the carboxyl ester lipase (CEL) gene determines proteotoxicity.J Biol Chem. 2021 Jan-Jun;296:100661. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2021.100661. Epub 2021 Apr 14. J Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 33862081 Free PMC article.
-
Twenty Years of AIRE.Front Immunol. 2018 Feb 12;9:98. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00098. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29483906 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The structure of the TH/INS locus and the parental allele expressed are not conserved between mammals.Heredity (Edinb). 2024 Jul;133(1):21-32. doi: 10.1038/s41437-024-00689-y. Epub 2024 Jun 4. Heredity (Edinb). 2024. PMID: 38834866 Free PMC article.
-
Functional Domains of Autoimmune Regulator (AIRE) Modulate INS-VNTR Transcription in Human Thymic Epithelial Cells.J Biol Chem. 2016 May 20;291(21):11313-22. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.722488. Epub 2016 Apr 5. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27048654 Free PMC article.
-
Aire and Fezf2, two regulators in medullary thymic epithelial cells, control autoimmune diseases by regulating TSAs: Partner or complementer?Front Immunol. 2022 Aug 30;13:948259. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.948259. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36110862 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Pugliese A: The insulin gene in type 1 diabetes. IUBMB Life 2005;57:463–468 - PubMed
-
- Bell GI, Selby MJ, Rutter WJ: The highly polymorphic region near the human insulin gene is composed of simple tandemly repeating sequences. Nature 1982;295:31–35 - PubMed
-
- Kennedy GC, German MS, Rutter WJ: The minisatellite in the diabetes susceptibility locus IDDM2 regulates insulin transcription. Nat Genet 1995;9:293–298 - PubMed
-
- Lucassen AM, Screaton GR, Julier C, Elliott TJ, Lathrop M, Bell JI: Regulation of insulin gene expression by the IDDM associated, insulin locus haplotype. Hum Mol Genet 1995;4:501–506 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

