Phenyl ring-substituted lobelane analogs: inhibition of [³H]dopamine uptake at the vesicular monoamine transporter-2
- PMID: 20876747
- PMCID: PMC3061534
- DOI: 10.1124/jpet.110.172882
Phenyl ring-substituted lobelane analogs: inhibition of [³H]dopamine uptake at the vesicular monoamine transporter-2
Abstract
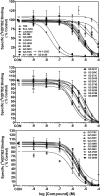
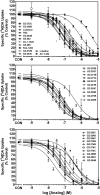
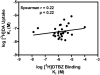
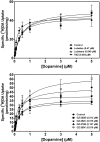
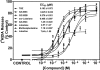
Lobeline attenuates the behavioral effects of methamphetamine via inhibition of the vesicular monoamine transporter (VMAT2). To increase selectivity for VMAT2, chemically defunctionalized lobeline analogs, including lobelane, were designed to eliminate nicotinic acetylcholine receptor affinity. The current study evaluated the ability of lobelane analogs to inhibit [³H]dihydrotetrabenazine (DTBZ) binding to VMAT2 and [³H]dopamine (DA) uptake into isolated synaptic vesicles and determined the mechanism of inhibition. Introduction of aromatic substituents in lobelane maintained analog affinity for the [³H]DTBZ binding site on VMAT2 and inhibitory potency in the [³H]DA uptake assay assessing VMAT2 function. The most potent (K(i) = 13-16 nM) analogs in the series included para-methoxyphenyl nor-lobelane (GZ-252B), para-methoxyphenyl lobelane (GZ-252C), and 2,4-dichlorphenyl lobelane (GZ-260C). Affinity of the analogs for the [³H]DTBZ binding site did not correlate with inhibitory potency in the [³H]DA uptake assay. It is noteworthy that the N-benzylindole-, biphenyl-, and indole-bearing meso-analogs 2,6-bis[2-(1-benzyl-1H-indole-3-yl)ethyl]-1-methylpiperidine hemifumarate (AV-1-292C), 2,6-bis(2-(biphenyl-4-yl)ethyl)piperidine hydrochloride (GZ-272B), and 2,6-bis[2-(1H-indole-3-yl)ethyl]-1-methylpiperidine monofumarate (AV-1-294), respectively] inhibited VMAT2 function (K(i) = 73, 127, and 2130 nM, respectively), yet had little to no affinity for the [³H]DTBZ binding site. These results suggest that the analogs interact at an alternate site to DTBZ on VMAT2. Kinetic analyses of [³H]DA uptake revealed a competitive mechanism for 2,6-bis(2-(4-methoxyphenyl)ethyl)piperidine hydrochloride (GZ-252B), 2,6-bis(2-(4-methoxyphenyl)ethyl)-1-methylpiperidine hydrochloride (GZ-252C), 2,6-bis(2-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)ethyl)piperidine hydrochloride (GZ-260C), and GZ-272B. Similar to methamphetamine, these analogs released [³H]DA from the vesicles, but with higher potency. In contrast to methamphetamine, these analogs had higher potency (>100-fold) at VMAT2 than DAT, predicting low abuse liability. Thus, modification of the lobelane molecule affords potent, selective inhibitors of VMAT2 function and reveals two distinct pharmacological targets on VMAT2.
Figures


References
-
- Andersen PH. (1987) Biochemical and pharmacological characterization of [3H]GBR 12935 binding in vitro to rat striatal membranes: labeling of the dopamine uptake complex. J Neurochem 48:1887–1896 - PubMed
-
- Briggs CA, McKenna DG. (1998) Activation and inhibition of the human α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor by agonists. Neuropharmacology 37:1095–1102 - PubMed
-
- Brown JM, Hanson GR, Fleckenstein AE. (2000) Methamphetamine rapidly decreases vesicular dopamine uptake. J Neurochem 74:2221–2223 - PubMed
-
- Cheng Y, Prusoff WH. (1973) Relationship between the inhibition constant (K1) and the concentration of inhibitor which causes 50 per cent inhibition (I50) of an enzymatic reaction. Biochem Pharmacol 22:3099–3108 - PubMed
-
- Decker MW, Majchrzak MJ, Arnerić SP. (1993) Effects of lobeline, a nicotinic receptor agonist, on learning and memory. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 45:571–576 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

