Ex-vivo gene therapy restores LEKTI activity and corrects the architecture of Netherton syndrome-derived skin grafts
- PMID: 20877344
- PMCID: PMC3034839
- DOI: 10.1038/mt.2010.201
Ex-vivo gene therapy restores LEKTI activity and corrects the architecture of Netherton syndrome-derived skin grafts
Abstract
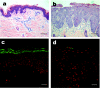
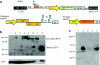
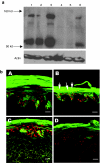
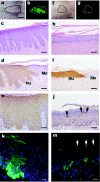
Netherton syndrome (NS) is a debilitating congenital skin disorder caused by mutations in the SPINK5 gene encoding the lymphoepithelial Kazal-type-related inhibitor (LEKTI). It is characterized by defective keratinization, recurrent infections, and hypernatraemic dehydration with a mortality rate of about 10% in the first year of life. Currently, there are no curative treatments for NS. We have developed a HIV-1 based, self-inactivating lentiviral vector to express SPINK5 in keratinocytes as part of an ex-vivo gene therapy strategy for NS. High transduction efficiency was achieved in NS keratinocytes and reconstitution of LEKTI expression was confirmed in previously deficient cells. These genetically corrected keratinocytes were further tested in an in vitro organotypic culture (OTC) system and in vivo mouse/human skin engraftment model. Results showed correction of epidermal architecture in both OTCs and regenerated skin grafts. Importantly, the results from corrected skin grafts indicated that even where detectable LEKTI expression was restored to a limited numbers of cells, a wider bystander benefit occurred around these small populations. As LEKTI is a secreted protein, the genetically modified graft may provide not only an immediate local protective barrier, but also act as a source of secreted LEKTI providing a generalized benefit following ex-vivo gene therapy.
Figures
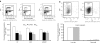

References
-
- Bitoun E, Micheloni A, Lamant L, Bonnart C, Tartaglia-Polcini A, Cobbold C, et al. LEKTI proteolytic processing in human primary keratinocytes, tissue distribution and defective expression in Netherton syndrome. Hum Mol Genet. 2003;12:2417–2430. - PubMed
-
- Chavanas S, Bodemer C, Rochat A, Hamel-Teillac D, Ali M, Irvine AD, et al. Mutations in SPINK5, encoding a serine protease inhibitor, cause Netherton syndrome. Nat Genet. 2000;25:141–142. - PubMed
-
- Borgoño CA, Michael IP, Komatsu N, Jayakumar A, Kapadia R, Clayman GL, et al. A potential role for multiple tissue kallikrein serine proteases in epidermal desquamation. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:3640–3652. - PubMed
-
- Descargues P, Deraison C, Prost C, Fraitag S, Mazereeuw-Hautier J, D'Alessio M, et al. Corneodesmosomal cadherins are preferential targets of stratum corneum trypsin- and chymotrypsin-like hyperactivity in Netherton syndrome. J Invest Dermatol. 2006;126:1622–1632. - PubMed
-
- Ishida-Yamamoto A, Deraison C, Bonnart C, Bitoun E, Robinson R, O'Brien TJ, et al. LEKTI is localized in lamellar granules, separated from KLK5 and KLK7, and is secreted in the extracellular spaces of the superficial stratum granulosum. J Invest Dermatol. 2005;124:360–366. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

