Micro-force sensing in robot assisted membrane peeling for vitreoretinal surgery
- PMID: 20879413
- PMCID: PMC3072686
- DOI: 10.1007/978-3-642-15711-0_38
Micro-force sensing in robot assisted membrane peeling for vitreoretinal surgery
Abstract
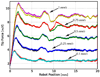
Vitreoretinal surgeons use 0.5 mm diameter instruments to manipulate delicate tissue inside the eye while applying imperceptible forces that can cause damage to the retina. We present a system which robotically regulates user-applied forces to the tissue, to minimize the risk of retinal hemorrhage or tear during membrane peeling, a common task in vitreoretinal surgery. Our research platform is based on a cooperatively controlled microsurgery robot. It integrates a custom micro-force sensing surgical pick, which provides conventional surgical function and real time force information. We report the development of a new phantom, which is used to assess robot control, force feedback methods, and our newly implemented auditory sensory substitution to specifically assist membrane peeling. Our findings show that auditory sensory substitution decreased peeling forces in all tests, and that robotic force scaling with audio feedback is the most promising aid in reducing peeling forces and task completion time.
Figures



References
-
- Gupta PK, Jensen PS, d Juan E. Surgical forces and tactile perception during retinal microsurgery. MICCAI. 99:1218–1225.
-
- Riviere C, Ang WT, Khosla P. Toward active tremor canceling in handheld microsurgical instruments. IEEE Tr. Rob. & Aut. 2003 Oct.vol. 19(5):793–800.
-
- Nakano T, Sugita N, Ueta T, Tamaki Y, Mitsuishi M. A parallel robot to assist vitreoretinal surgery. JCARS. 2009 - PubMed
-
- Mitchell B, Koo J, Iordachita M, Kazanzides P, Kapoor A, Handa J, Hager G, Taylor R. Development and application of a new steady-hand manipulator for retinal surgery. IEEE ICRA. 2007:623–629.
-
- Berkelman P, Whitcomb L, Taylor R, Jensen P. A miniature microsurgical instrument tip force sensor for enhanced force feedback during robot-assisted manipulation. IEEE TRA. 2003 Oct.19(5):917–921.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
