Rheumatoid arthritis and salivary biomarkers of periodontal disease
- PMID: 20880053
- PMCID: PMC2980566
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-051X.2010.01625.x
Rheumatoid arthritis and salivary biomarkers of periodontal disease
Abstract
Aim: To test the hypothesis that rheumatoid arthritis (RA) influenced levels of salivary biomarkers of periodontal disease.
Methods: Medical assessments, periodontal examinations and pain ratings were obtained from 35 RA, 35 chronic periodontitis and 35 age- and gender-matched healthy controls in a cross-sectional, case-controlled study. Unstimulated whole saliva samples were analysed for interleukin-1β (IL-1β), matrix metalloproteinase-8 (MMP-8) and tumour necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) concentrations.
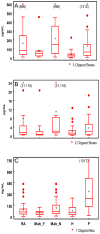
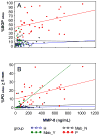
Results: The arthritis and healthy groups had significantly less oral disease than the periodontitis group (P<0.0001), with the arthritis group having significantly more sites bleeding on probing (BOP) than matched controls (P=0.012). Salivary levels of MMP-8 and IL-1β were significantly elevated in the periodontal disease group (P<0.002), and IL-1β was the only biomarker with significantly higher levels in the arthritis group compared with controls (P=0.002). Arthritis patients receiving anti-TNF-α antibody therapy had significantly lower IL-1β and TNF-α levels compared with arthritis patients not on anti-TNF-α therapy (P=0.016, 0.024) and healthy controls (P<0.001, P=0.011), respectively.
Conclusion: RA patients have higher levels of periodontal inflammation than healthy controls, i.e., an increased BOP. Systemic inflammation appears to influence levels of select salivary biomarkers of periodontal disease, and anti-TNF-α antibody-based disease-modifying therapy significantly lowers salivary IL-1β and TNF-α levels in RA.
© 2010 John Wiley & Sons A/S.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: The authors report no conflicts of interest related to this study.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evaluation of salivary interleukin-17 and developmental endothelial locus-1 in patients with periodontitis with and without type 2 diabetes mellitus.J Periodontol. 2025 May;96(5):407-417. doi: 10.1002/JPER.23-0720. Epub 2024 Sep 23. J Periodontol. 2025. PMID: 39311693
-
Anti-tumor necrosis factor-alpha therapy and periodontal parameters in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.J Periodontol. 2009 Sep;80(9):1414-20. doi: 10.1902/jop.2009.090015. J Periodontol. 2009. PMID: 19722791
-
Correlations between pentraxin 3 or cytokine levels in gingival crevicular fluid and clinical parameters of chronic periodontitis.Odontology. 2012 Jul;100(2):215-21. doi: 10.1007/s10266-011-0042-1. Epub 2011 Sep 20. Odontology. 2012. PMID: 21932007
-
Influence of anti-rheumatic agents on the periodontal condition of patients with rheumatoid arthritis and periodontitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis.J Periodontal Res. 2021 Dec;56(6):1099-1115. doi: 10.1111/jre.12925. Epub 2021 Sep 12. J Periodontal Res. 2021. PMID: 34514591
-
Changes in Inflammatory Cytokines in Saliva after Non-Surgical Periodontal Therapy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 Dec 29;18(1):194. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18010194. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. PMID: 33383828 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
In vitro activity of anti-rheumatic drugs on release of pro-inflammatory cytokines from oral cells in interaction with microorganisms.Front Oral Health. 2022 Sep 2;3:960732. doi: 10.3389/froh.2022.960732. eCollection 2022. Front Oral Health. 2022. PMID: 36118051 Free PMC article.
-
Determining the biological associates of acute cold pressor post-encoding stress effects on human memory: The role of salivary interleukin-1β.Brain Behav Immun. 2019 Oct;81:178-187. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2019.06.011. Epub 2019 Jun 7. Brain Behav Immun. 2019. PMID: 31176727 Free PMC article.
-
Does periodontitis represent a risk factor for rheumatoid arthritis? A systematic review and meta-analysis.Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis. 2019 Jul 9;11:1759720X19858514. doi: 10.1177/1759720X19858514. eCollection 2019. Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis. 2019. PMID: 31316593 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Levels of Selected Matrix Metalloproteinases, Their Inhibitors in Saliva, and Oral Status in Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis Patients vs. Healthy Controls.Biomed Res Int. 2019 Oct 28;2019:7420345. doi: 10.1155/2019/7420345. eCollection 2019. Biomed Res Int. 2019. PMID: 31781639 Free PMC article.
-
Porphyromonas gingivalis oral infection exacerbates the development and severity of collagen-induced arthritis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2013 Nov 12;15(6):R186. doi: 10.1186/ar4376. Arthritis Res Ther. 2013. PMID: 24456966 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Armitage GC. Development of a classification system for periodontal diseases and conditions. Ann Periodontol. 1999;4:1–6. - PubMed
-
- Armitage GC. Periodontal diagnoses and classification of periodontal diseases. Periodontol 2000. 2004;34:9–21. - PubMed
-
- Arnett FC, Edworthy SM, Bloch DA, McShane DJ, Fries JF, Cooper NS, Healey LA, Kaplan SR, Liang MH, Luthra HS, et al. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988;31:315–324. - PubMed
-
- Assuma R, Oates T, Cochran D, Amar S, Graves DT. IL-1 and TNF antagonists inhibit the inflammatory response and bone loss in experimental periodontitis. J Immunol. 1998;160:403–409. - PubMed
-
- Azuma Y, Kaji K, Katogi R, Takeshita S, Kudo A. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha induces differentiation of and bone resorption by osteoclasts. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:4858–4864. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

