Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging for tumour response assessment: why, when and how?
- PMID: 20880779
- PMCID: PMC2967137
- DOI: 10.1102/1470-7330.2010.9032
Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging for tumour response assessment: why, when and how?
Abstract
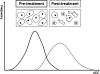
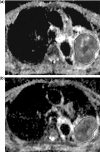
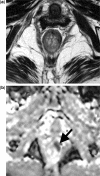
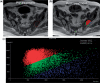
Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (DWI) is increasingly being used to assess tumour response to a variety of anticancer treatments. The technique is quick to perform without the need for administration of exogenous contrast medium, and enables the apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) of tissues to be quantified. Studies have shown that ADC increases in response to a variety of treatments including chemotherapy, radiotherapy, minimally invasive therapies and novel therapeutics. In this article, we review the rationale of applying DWI for tumour assessment, the evidence for ADC measurements in relation to specific treatments and some of the practical considerations for using ADC to evaluate treatment response.
Figures



References
-
- Miller AB, Hoogstraten B, Staquet M, et al. Reporting results of cancer treatment. Cancer. 1981;47:207–14. doi:10.1002/1097-0142(19810101)47:1<207::AID-CNCR2820470134>3.0.CO;2-6. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Eisenhauer EA, Therasse P, Bogaerts J, et al. New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours: revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1) Eur J Cancer. 2009;45:228–47. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2008.10.026. PMid:19097774. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Therasse P, Arbuck SG, Eisenhauer EA, et al. New guidelines to evaluate the response to treatment in solid tumors. European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer, National Cancer Institute of the United States, National Cancer Institute of Canada. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2000;92:205–16. doi:10.1093/jnci/92.3.205. PMid:10655437. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Harry VN, Semple SI, Parkin DE, et al. Use of new imaging techniques to predict tumour response to therapy. Lancet Oncol. 2010;11:92–102. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(09)70190-1. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
