Blind subjects implanted with the Argus II retinal prosthesis are able to improve performance in a spatial-motor task
- PMID: 20881025
- PMCID: PMC3345188
- DOI: 10.1136/bjo.2010.179622
Blind subjects implanted with the Argus II retinal prosthesis are able to improve performance in a spatial-motor task
Abstract
Background/aims: To determine to what extent subjects implanted with the Argus II retinal prosthesis can improve performance compared with residual native vision in a spatial-motor task.
Methods: High-contrast square stimuli (5.85 cm sides) were displayed in random locations on a 19″ (48.3 cm) touch screen monitor located 12″ (30.5 cm) in front of the subject. Subjects were instructed to locate and touch the square centre with the system on and then off (40 trials each). The coordinates of the square centre and location touched were recorded.
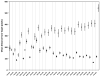
Results: Ninety-six percent (26/27) of subjects showed a significant improvement in accuracy and 93% (25/27) show a significant improvement in repeatability with the system on compared with off (p<0.05, Student t test). A group of five subjects that had both accuracy and repeatability values <250 pixels (7.4 cm) with the system off (ie, using only their residual vision) was significantly more accurate and repeatable than the remainder of the cohort (p<0.01). Of this group, four subjects showed a significant improvement in both accuracy and repeatability with the system on.
Conclusion: In a study on the largest cohort of visual prosthesis recipients to date, we found that artificial vision augments information from existing vision in a spatial-motor task. Clinical trials registry no NCT00407602.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
-
- Marc RE, Jones BW, Watt CB, et al. Neural remodeling in retinal degeneration. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2003;22:607–55. - PubMed
-
- Jones BW, Marc RE. Retinal remodeling during retinal degeneration. Exp Eye Res. 2005;81:123–37. - PubMed
-
- Santos A, Humayun MS, de Juan E, Jr, et al. Preservation of the inner retina in retinitis pigmentosa. a morphometric analysis. Arch Ophthalmol. 1997;115:511–15. - PubMed
-
- Stone JL, Barlow WE, Humayun MS, et al. Morphometric analysis of macular photoreceptors and ganglion cells in retinas with retinitis pigmentosa. Arch Ophthalmol. 1992;110:1634–9. - PubMed
-
- Jensen RJ, Ziv OR, Rizzo JF, 3rd, et al. Spatiotemporal aspects of pulsed electrical stimuli on the responses of rabbit retinal ganglion cells. Exp Eye Res. 2009;89:972–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
