NHANES monitoring of serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D: a roundtable summary
- PMID: 20881084
- PMCID: PMC2955879
- DOI: 10.3945/jn.110.121483
NHANES monitoring of serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D: a roundtable summary
Abstract
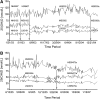
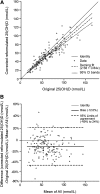
A roundtable to discuss monitoring of serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D [25(OH)D] in the NHANES was held in late July 2009. Topics included the following: 1) options for dealing with assay fluctuations in serum 25(OH)D in the NHANES conducted between 1988 and 2006; 2) approaches for transitioning between the RIA used in the NHANES between 1988 and 2006 to the liquid chromatography tandem MS (LC-MS/MS) measurement procedure to be used in NHANES 2007 and later; 3) approaches for integrating the recently available standard reference material for vitamin D in human serum (SRM 972) from the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) into the NHANES; 4) questions regarding whether the C-3 epimer of 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 [3-epi-25(OH)D3] should be measured in NHANES 2007 and later; and 5) identification of research and educational needs. The roundtable experts agreed that the NHANES data needed to be adjusted to control for assay fluctuations and offered several options for addressing this issue. The experts suggested that the LC-MS/MS measurement procedure developed by NIST could serve as a higher order reference measurement procedure. They noted the need for a commutability study for the recently released NIST SRM 972 across a range of measurement procedures. They suggested that federal agencies and professional organizations work with manufacturers to improve the quality and comparability of measurement procedures across all laboratories. The experts noted the preliminary nature of the evidence of the 3-epi-25(OH)D3 but felt that it should be measured in 2007 NHANES and later.
Conflict of interest statement
Author disclosures: E. A. Yetley, C. M. Pfeiffer, R. L. Schleicher, K. W. Phinney, D. A. Lacher, S. Christakos, J. H. Eckfeldt, J. C. Fleet, G. Howard, S. L. Hui, G. L. Lensmeyer, J. Massaro, M. Peacock, B. Rosner, D. Wiebe, R. L. Bailey, P. M. Coates, A. C. Looker, C. Sempos, C. L. Johnson, and M. F. Picciano, no conflicts of interest. A. N. Hoofnagle reports funding via the Nutrition and Obesity Research Center at the University of Washington (NIH grant 5P30 DK035816).
Figures
References
-
- National Center for Health Statistics Analytical note for NHANES 2000–2006 and NHANES III (1988–1994) 25-hydroxyvitamin D analysis. Hyattsville (MD): National Center for Health Statistics [cited 2010 Jan 28] Available from: http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/nhanes/nhanes3/VitaminD_analyticnote.pdf
-
- Yetley EA. Assessing the vitamin D status of the US population. Am J Clin Nutr. 2008;88:S558–64 - PubMed
-
- Brannon PM, Yetley EA, Bailey RL, Picciano MF. Summary of roundtable discussion on vitamin D research needs. Am J Clin Nutr. 2008;88:S587–92 - PubMed
-
- Myers GL, Kimberly MM, Waymack PP, Smith SJ, Cooper GR, Sampson EJ. A reference method laboratory network for cholesterol: a model for standardization and improvement of clinical laboratory measurements. Clin Chem. 2000;46:1762–72 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

