Membrane estrogen receptors stimulate intracellular calcium release and progesterone synthesis in hypothalamic astrocytes
- PMID: 20881113
- PMCID: PMC2957903
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1158-10.2010
Membrane estrogen receptors stimulate intracellular calcium release and progesterone synthesis in hypothalamic astrocytes
Abstract
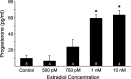
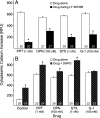
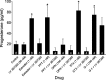
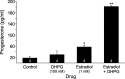
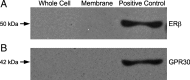
In hypothalamic astrocytes obtained from adult female rats, estradiol rapidly increased free cytoplasmic calcium concentrations ([Ca(2+)](i)) that facilitate progesterone synthesis. The present study demonstrated that estradiol (1 nm) significantly and maximally stimulated progesterone synthesis within 5 min, supporting a rapid, nongenomic mechanism. The group I metabotropic glutamate receptor (mGluR1a) antagonist LY 367385 [(S)-(+)-a-amino-4-carboxy-2-methylbenzeneacetic acid] attenuated both the estradiol-induced [Ca(2+)](i) release and progesterone synthesis. To investigate membrane-associated estrogen receptors (mERs), agonists for ERα, ERβ, STX-activated protein, and GPR30 were compared. The selective ERα agonist propylpyrazole triole (PPT) and STX most closely mimicked the estradiol-induced [Ca(2+)](i) responses, where PPT was more potent but less efficacious than STX. Only high doses (100 nm) of selective ERβ agonist diarylpropionitrile (DPN) and GPR30 agonist G-1 induced estradiol-like [Ca(2+)](i) responses. With the exception of DPN (even at 100 nm), all agonists stimulated progesterone synthesis. The PPT- and STX-induced [Ca(2+)](i) release and progesterone synthesis were blocked by LY 367385. While the G-1-stimulated [Ca(2+)](i) release was blocked by LY 367385, progesterone synthesis was not. Since GPR30 was detected intracellularly but not in the membrane, we interpreted these results to suggest that G-1 could activate mGluR1a on the membrane and GPR30 on the smooth endoplasmic reticulum to release intracellular calcium. Although STX and G-1 maximally stimulated [Ca(2+)](i) release in astrocytes from estrogen receptor-α knock-out (ERKO) mice, estradiol in vivo did not stimulate progesterone synthesis in the ERKO mice. Together, these results indicate that mERα is mainly responsible for the rapid, membrane-initiated estradiol-signaling that leads to progesterone synthesis in hypothalamic astrocytes.
Figures


References
-
- Beyer C, Raab H. Nongenomic effects of oestrogen: embryonic mouse midbrain neurones respond with a rapid release of calcium from intracellular stores. Eur J Neurosci. 1998;10:255–262. - PubMed
-
- Bologa CG, Revankar CM, Young SM, Edwards BS, Arterburn JB, Kiselyov AS, Parker MA, Tkachenko SE, Savchuck NP, Sklar LA, Oprea TI, Prossnitz ER. Virtual and biomolecular screening converge on a selective agonist for GPR30. Nat Chem Biol. 2006;2:207–212. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
