Interfering with resistance to smoothened antagonists by inhibition of the PI3K pathway in medulloblastoma
- PMID: 20881279
- PMCID: PMC3422576
- DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3001599
Interfering with resistance to smoothened antagonists by inhibition of the PI3K pathway in medulloblastoma
Abstract
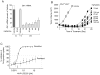
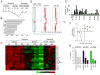
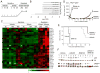
The malignant brain cancer medulloblastoma is characterized by mutations in Hedgehog (Hh) signaling pathway genes, which lead to constitutive activation of the G protein (heterotrimeric guanosine triphosphate-binding protein)-coupled receptor Smoothened (Smo). The Smo antagonist NVP-LDE225 inhibits Hh signaling and induces tumor regression in animal models of medulloblastoma. However, evidence of resistance was observed during the course of treatment. Molecular analysis of resistant tumors revealed several resistance mechanisms. We noted chromosomal amplification of Gli2, a downstream effector of Hh signaling, and, more rarely, point mutations in Smo that led to reactivated Hh signaling and restored tumor growth. Analysis of pathway gene expression signatures also, unexpectedly, identified up-regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) signaling in resistant tumors as another potential mechanism of resistance. Probing the relevance of increased PI3K signaling, we demonstrated that addition of the PI3K inhibitor NVP-BKM120 or the dual PI3K-mTOR (mammalian target of rapamycin) inhibitor NVP-BEZ235 to the initial treatment with the Smo antagonist markedly delayed the development of resistance. Our findings may be useful in informing treatment strategies for medulloblastoma.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Varjosalo M, Taipale J. Hedgehog: functions and mechanisms. Genes & Development. 2008;22:2454–2472. - PubMed
-
- Romer JT, Kimura H, Magdaleno S, Sasai K, Fuller C, Baines H, Connelly M, Stewart CF, Gould S, Rubin LL, Curran T. Suppression of the Shh pathway using a small molecule inhibitor eliminates medulloblastoma in Ptc1(+/−)p53(−/−) mice. Cancer Cell. 2004;6:229–40. - PubMed
-
- Engelman JA, Settleman J. Acquired resistance to tyrosine kinase inhibitors during cancer therapy. Current Opinion in Genetics & Development. 2008;18:73–79. - PubMed
-
- Pan S, Wu X, Jiang J, Gao W, Wan Y, Cheng D, Han D, Liu J, Englund NP, Wang Y, Peukert S, Miller-Moslin K, Yuan J, Guo R, Matsumoto M, Vattay A, Jiang Y, Tsao J, Sun F, Pferdekamper AC, Dodd S, Tuntland T, Maniara W, Kelleher JF, Yao Ym, Warmuth M, Williams J, Dorsch M. ACS Medicinal Chemistry Letters. 2010. Discovery of NVP-LDE225, a Potent and Selective Smoothened Antagonist. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

