The Role of Type 1 Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors in the Generation of Dorsal Root Reflexes Induced by Acute Arthritis or the Spinal Infusion of 4-Aminopyridine in the Anesthetized Rat
- PMID: 20882110
- PMCID: PMC2946106
- DOI: 10.1016/S1526-5900(00)90100-7
The Role of Type 1 Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors in the Generation of Dorsal Root Reflexes Induced by Acute Arthritis or the Spinal Infusion of 4-Aminopyridine in the Anesthetized Rat
Abstract
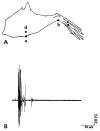
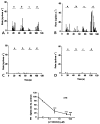
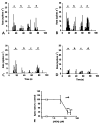
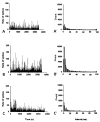
Antidromically propagated action potentials can be recorded in the proximal end of the severed medial articular nerve (MAN) on mechanical stimulation of an inflamed knee in rats and are referred to as dorsal root reflex (DRR) activity. The absence of DRR activity in normal rats suggests that the activity could be the result of hyperexcitability of spinal neurons induced by inflammation. In this study, the role of spinal type 1 metabotropic glutamate (mGlu(1)) receptors in the generation of DRR activity in the MAN during acute knee inflammation was investigated. Four hours after an injection of a mixture of kaolin and carrageenan (k/c) into a knee joint, DRR activity could be evoked in the ipsilateral MAN by mechanical stimulation of the inflamed limb. Spinal application of a selective mGlu(1) receptor antagonist, [RS]-1-Aminoindan-1,5-dicarboxylic acid/UPF 523 (AIDA), or a potent, but less specific mGlu(1) receptor antagonist, LY393053, both depressed the DRR activity significantly. AIDA and LY39053 had no effect on recordings in the MAN from noninflamed control animals. However, spinal administration of AIDA did suppress DRR activity generated by infusion of 4-aminopyridine (4-AP), a K(+) channel blocker, into the dorsal horn of noninflamed animals. These observations suggest that mGlu(1) receptors support the generation of DRR activity in the MAN following sensitization of spinal cord neurons.
Figures
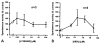
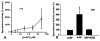
Similar articles
-
Group I metabotropic glutamate receptor antagonists block secondary thermal hyperalgesia in rats with knee joint inflammation.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2002 Jan;300(1):149-56. doi: 10.1124/jpet.300.1.149. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2002. PMID: 11752110
-
Effects of N- and L-type calcium channel antagonists on the responses of nociceptive spinal cord neurons to mechanical stimulation of the normal and the inflamed knee joint.J Neurophysiol. 1996 Dec;76(6):3740-9. doi: 10.1152/jn.1996.76.6.3740. J Neurophysiol. 1996. PMID: 8985872
-
The role of glutamate and GABA receptors in the generation of dorsal root reflexes by acute arthritis in the anaesthetized rat.J Physiol. 1995 Apr 15;484 ( Pt 2)(Pt 2):437-45. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1995.sp020676. J Physiol. 1995. PMID: 7602536 Free PMC article.
-
Fiber types contributing to dorsal root reflexes induced by joint inflammation in cats and monkeys.J Neurophysiol. 1995 Sep;74(3):981-9. doi: 10.1152/jn.1995.74.3.981. J Neurophysiol. 1995. PMID: 7500166
-
Group II and group III metabotropic glutamate receptor agonists depress synaptic transmission in the rat spinal cord dorsal horn.Neuroscience. 2000;100(2):393-406. doi: 10.1016/s0306-4522(00)00269-4. Neuroscience. 2000. PMID: 11008177
Cited by
-
Glial contributions to visceral pain: implications for disease etiology and the female predominance of persistent pain.Transl Psychiatry. 2016 Sep 13;6(9):e888. doi: 10.1038/tp.2016.168. Transl Psychiatry. 2016. PMID: 27622932 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chapter 9 The dorsal horn and hyperalgesia.Handb Clin Neurol. 2006;81:103-25. doi: 10.1016/S0072-9752(06)80013-8. Handb Clin Neurol. 2006. PMID: 18808831 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
A peripheral neuroimmune link: glutamate agonists upregulate NMDA NR1 receptor mRNA and protein, vimentin, TNF-alpha, and RANTES in cultured human synoviocytes.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2010 Mar;298(3):R584-98. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00452.2009. Epub 2009 Dec 9. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20007519 Free PMC article.
-
Ketamine and peripheral inflammation.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2013 Jun;19(6):403-10. doi: 10.1111/cns.12104. Epub 2013 Apr 10. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2013. PMID: 23574634 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sluka KA, Westlund KN. Behavioral and immunohistochemical changes in an experimental arthritis model in rats. Pain. 1993;55(3):367–377. - PubMed
-
- Sluka KA, Westlund KN. Spinal cord amino acid release and content in an arthritis model-the effects of pretreatment with non-NMDA, NMDA and NK1 receptor antagonists. Brain Res. 1993;627:89–103. - PubMed
-
- Sorkin LS, Westlund KN, Sluka KA, Dougherty PM, Willis WD. Neural changes in acute arthiritis in monkeys IV Time-course of amino acid release into the lumbar dorsal horn. Brain Res Rev. 1992;17:39–50. - PubMed
-
- Neugebauer V, Schaible HG. Evidence for a central component in the sensitization of spinal neurons with joint input during development of acute arthritis in cat’s knee. J Neurophysiol. 1990;64:299–311. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
