Hydrophobic, Non-Hydrogen-Bonding Bases and Base Pairs in DNA
- PMID: 20882111
- PMCID: PMC2946113
- DOI: 10.1021/ja00112a001
Hydrophobic, Non-Hydrogen-Bonding Bases and Base Pairs in DNA
Abstract
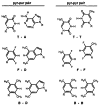
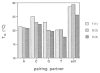
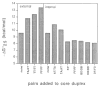
We report the properties of hydrophobic isosteres of pyrimidines and purines in synthetic DNA duplexes. Phenyl nucleosides 1 and 2 are nonpolar isosteres of the natural thymidine nucleoside, and indole nucleoside 3 is an analog of the complementary purine 2-aminodeoxyadenosine. The nucleosides were incorporated into synthetic oligodeoxynucleotides and were paired against each other and against the natural bases. Thermal denaturation experiments were used to measure the stabilities of the duplexes at neutral pH. It is found that the hydrophobic base analogs are nonselective in pairing with the four natural bases but selective for pairing with each other rather than with the natural bases. For example, compound 2 selectively pairs with itself rather than with A, T, G, or C; the magnitude of this selectivity is found to be 6.5-9.3 °C in Tm or 1.5-1.8 kcal/mol in free energy (25 °C). All possible hydrophobic pairing combinations of 1, 2, and 3 were examined. Results show that the pairing affinity depends on the nature of the pairs and on position in the duplex. The highest affinity pairs are found to be the 1-1 and 2-2 self-pairs and the 1-2 heteropair. The best stabilization occurs when the pairs are placed at the ends of duplexes rather than internally; the internal pairs may be destabilized by imperfect steric mimicry which leads to non-ideal duplex structure. In some cases the hydrophobic pairs are significantly stabilizing to the DNA duplex; for example, when situated at the end of a duplex, the 1-1 pair is more stabilizing than a T-A pair. When situated internally, the affinity of the 1-1 pair is the same as, or slightly better than, the analogous T-T mismatch pair, which is known to have two hydrogen bonds. The studies raise the possibility that hydrogen bonds may not always be required for the formation of stable duplex DNA-like structure. In addition, the results point out the importance of solvation and desolvation in natural base pairing, and lend new support to the idea that hydrogen bonds in DNA may be more important for specificity of pairing than for affinity. Finally, the study raises the possibility of using these or related base pairs to expand the genetic code beyond the natural A-T and G-C pairs.
Figures



Similar articles
-
New base pairing motifs. The synthesis and thermal stability of oligodeoxynucleotides containing imidazopyridopyrimidine nucleosides with the ability to form four hydrogen bonds.J Am Chem Soc. 2003 Aug 20;125(33):9970-82. doi: 10.1021/ja0347686. J Am Chem Soc. 2003. PMID: 12914460
-
The steric hypothesis for DNA replication and fluorine hydrogen bonding revisited in light of structural data.Acc Chem Res. 2012 Aug 21;45(8):1237-46. doi: 10.1021/ar200303k. Epub 2012 Apr 23. Acc Chem Res. 2012. PMID: 22524491 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pyrimidine.pyrimidine base-pair mismatches in DNA. A nuclear magnetic resonance study of T.T pairing at neutral pH and C.C pairing at acidic pH in dodecanucleotide duplexes.J Mol Biol. 1988 Jul 5;202(1):139-55. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90526-8. J Mol Biol. 1988. PMID: 2845094
-
Measurement and theory of hydrogen bonding contribution to isosteric DNA base pairs.J Am Chem Soc. 2012 Feb 15;134(6):3154-63. doi: 10.1021/ja210475a. Epub 2012 Feb 2. J Am Chem Soc. 2012. PMID: 22300089 Free PMC article.
-
Binding of metal ions by pyrimidine base pairs in DNA duplexes.Chem Soc Rev. 2011 Dec;40(12):5855-66. doi: 10.1039/c1cs15149e. Epub 2011 Aug 8. Chem Soc Rev. 2011. PMID: 21826352 Review.
Cited by
-
Solution Structure of a Nonpolar, Non-Hydrogen-Bonded Base Pair Surrogate in DNA.J Am Chem Soc. 2000 Jul 26;122(29):6841-6847. doi: 10.1021/ja994164v. J Am Chem Soc. 2000. PMID: 20882115 Free PMC article.
-
High-fidelity in vivo replication of DNA base shape mimics without Watson-Crick hydrogen bonds.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Apr 15;100(8):4469-73. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0837277100. Epub 2003 Apr 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003. PMID: 12676985 Free PMC article.
-
Survey and summary: The applications of universal DNA base analogues.Nucleic Acids Res. 2001 Jun 15;29(12):2437-47. doi: 10.1093/nar/29.12.2437. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001. PMID: 11410649 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetics just got SEXY: Sequences encoding XY.Bioengineered. 2014 Jul-Aug;5(4):214-5. doi: 10.4161/bioe.29306. Epub 2014 May 21. Bioengineered. 2014. PMID: 24847983 Free PMC article.
-
Processive Incorporation of Deoxynucleoside Triphosphate Analogs by Single-Molecule DNA Polymerase I (Klenow Fragment) Nanocircuits.J Am Chem Soc. 2015 Aug 5;137(30):9587-94. doi: 10.1021/jacs.5b02074. Epub 2015 Jul 17. J Am Chem Soc. 2015. PMID: 26147714 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Watson JD, Crick FHC. Nature. 1953;171:737–738. - PubMed
-
- Schultz GE, Schirmer RH. Principles of Protein Structure. Springer-Verlag; New York: 1979. pp. 149–165.
-
- Klotz IM, Frantzen JS. J Am Chem Soc. 1962;84:3461–3466.
- Cantor CR, Schimmel PR. Biophysical Chemistry Part I: The Conformation of Biological Macromolecules. W. H. Freeman; San Francisco: 1980. pp. 277–279.
-
- Turner DH, Sugimoto N, Kierzek R, Dreiker SD. J Am Chem Soc. 1987;109:3783–3785.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
