Diffusion tensor tractography of the human brain cortico-ponto-cerebellar pathways: a quantitative preliminary study
- PMID: 20882611
- PMCID: PMC4492525
- DOI: 10.1002/jmri.22330
Diffusion tensor tractography of the human brain cortico-ponto-cerebellar pathways: a quantitative preliminary study
Abstract
Purpose: To investigate the utility of diffusion tensor tractography at 1mm slice thickness to map and quantify the whole trajectory of different cortico-ponto-cerebellar pathways of the healthy adult human brain.
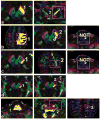
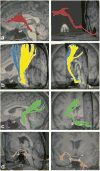
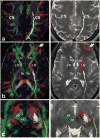
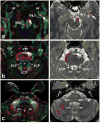
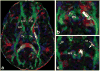
Materials and methods: This work was approved by the local Institutional Review Board, and was Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) compliant. Five healthy right-handed men (age range, 24-37 years) were studied and written informed consent was obtained. Diffusion tensor imaging data acquired with 1-mm slice thickness at a 3.0 Tesla (T) clinical MRI scanner were prepared and analyzed using tractography methods to reconstruct the cortico-ponto-cerebellar pathways which included the fronto-ponto-cerebellar, parieto-ponto-cerebellar, occipito-ponto-cerebellar, and temporo-ponto-cerebellar tracts.
Results: We demonstrate the feasibility of tractographic mapping and quantification of the four cortico-ponto-cerebellar system components based on their cortical connections in the healthy human brain using DTI data with thin 1-mm sections.
Conclusion: In vivo quantification of different cortico-ponto-cerebellar pathways based on cortical connection is feasible, using 1-mm slices at 3.0T.
Figures


References
-
- Afifi AK, Bergman RA. Text and atlas. New York: McGraw-Hill; 1998. Functional neuroanatomy; p. 730.
-
- Nolte J. An introduction to its functional anatomy. 5. St. Louis: MO: Mosby; 2002. The human brain; p. 650.
-
- Kitamura K, Nakayama K, Kosaka S, et al. Diffusion tensor imaging of the cortico-ponto-cerebellar pathway in patients with adult-onset ataxic neurodegenerative disease. Neuroradiology. 2008;50:285–292. - PubMed
-
- Adachi M, Hosoya T, Yamaguchi K, et al. Diffusion- and T2- weighted MRI of the transverse pontine fibers in spinocerebellar degeneration. Neuroradiology. 2000;42:803–809. - PubMed
-
- Blain CR, Barker GJ, Jarosz JM, et al. Measuring brain stem and cerebellar damage in parkinsonian syndromes using diffusion tensor MRI. Neurology. 2006;67:2199–2205. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

