Design and synthesis of phospholipase C and A2-activatable near-infrared fluorescent smart probes
- PMID: 20882956
- PMCID: PMC2958237
- DOI: 10.1021/bc100271v
Design and synthesis of phospholipase C and A2-activatable near-infrared fluorescent smart probes
Abstract
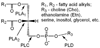
The primary focus of this work was to develop activatable probes suitable for in vivo detection of phospholipase activity. Phospholipases (PLs) are ubiquitous enzymes that perform a number of critical regulatory functions. They catalyze phospholipid breakdown and are categorized as A(1), A(2) (PLA(2)), C (PLC), and D (PLD) based on their site of action. Here, we report the design, synthesis, and characterization of self-quenching reporter probes that release fluorescent moieties upon cleavage with PLA(2) or PLC. A series of phospholipids were synthesized bearing the NIR fluorophore pyropheophorbide a (Pyro) at the sn-2 position. Fluorescence quenching was achieved by attachment of either a positively charged black hole quencher-3 (BHQ-3) to the phospholipid headgroup or another neutral Pyro moiety at the sn-1 position. The specificity to different phospholipases was modulated by insertion of spacers (C(6), C(12)) between Pyro and the lipid backbone. The specificity of the quenched fluorescent phospholipids was assayed on a plate reader against a number of phospholipases and compared with two commercial probes bearing the visible fluorophore BODIPY. While PyroC(6)-PyroC(6)-PtdCho revealed significant background fluorescence, and a 10% fluorescence increase under the action of PLA(2), Pyro-PtdEtn-BHQ demonstrated high selective sensitivity to PLC, particularly to the PC-PLC isoform, and its sensitivity to PLA(2) was negligible due to steric hindrance at the sn-2 position. In contrast, the C(12)-spacered PyroC(12)-PtdEtn-BHQ demonstrated a remarkable selectivity for PLA(2) and the best relative PLA(2)/PLC sensitivity, significantly outperforming previously known probes. These results open an avenue for future in vivo experiments and for new probes to detect PL activity.
Figures

Similar articles
-
In vivo detection of phospholipase C by enzyme-activated near-infrared probes.Bioconjug Chem. 2011 Dec 21;22(12):2434-43. doi: 10.1021/bc200242v. Epub 2011 Nov 29. Bioconjug Chem. 2011. PMID: 22034913 Free PMC article.
-
A quantitative continuous enzyme assay of intramolecularly quenched fluorogenic phospholipase substrates for molecular imaging.Anal Biochem. 2012 Mar 15;422(2):96-102. doi: 10.1016/j.ab.2011.12.009. Epub 2011 Dec 9. Anal Biochem. 2012. PMID: 22230285 Free PMC article.
-
Nonprotecting Group Synthesis of a Phospholipase C Activatable Probe with an Azo-Free Quencher.ACS Omega. 2018 Jun 30;3(6):6867-6873. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.8b00635. Epub 2018 Jun 25. ACS Omega. 2018. PMID: 29978148 Free PMC article.
-
Signaling and interplay mediated by phospholipases A2, C, and D in LA-N-1 cell nuclei.Reprod Nutr Dev. 2005 Sep-Oct;45(5):613-31. doi: 10.1051/rnd:2005049. Reprod Nutr Dev. 2005. PMID: 16188211 Review.
-
Involvement of cytosolic phospholipase A(2), calcium independent phospholipase A(2) and plasmalogen selective phospholipase A(2) in neurodegenerative and neuropsychiatric conditions.Curr Med Chem. 2010;17(25):2746-63. doi: 10.2174/092986710791859289. Curr Med Chem. 2010. PMID: 20586719 Review.
Cited by
-
1,7-Bis-(N,N-dialkylamino)perylene Bisimides: Facile Synthesis and Characterization as Near-Infrared Fluorescent Dyes.Materials (Basel). 2014 Nov 24;7(11):7548-7565. doi: 10.3390/ma7117548. Materials (Basel). 2014. PMID: 28788262 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo detection of phospholipase C by enzyme-activated near-infrared probes.Bioconjug Chem. 2011 Dec 21;22(12):2434-43. doi: 10.1021/bc200242v. Epub 2011 Nov 29. Bioconjug Chem. 2011. PMID: 22034913 Free PMC article.
-
Gamma-irradiation produces active chlorine species (ACS) in physiological solutions: Secoisolariciresinol diglucoside (SDG) scavenges ACS - A novel mechanism of DNA radioprotection.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016 Sep;1860(9):1884-97. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2016.05.037. Epub 2016 May 31. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016. PMID: 27261092 Free PMC article.
-
Scalable Synthesis and Purification of Acetylated Phosphatidyl Choline Headgroup.Org Process Res Dev. 2017 Feb 17;21(2):177-181. doi: 10.1021/acs.oprd.6b00261. Epub 2017 Jan 24. Org Process Res Dev. 2017. PMID: 30792570 Free PMC article.
-
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Imaging Using a Phospholipase A2 Activatable Fluorophore.Chem Biomed Imaging. 2024 Jun 20;2(7):490-500. doi: 10.1021/cbmi.4c00026. eCollection 2024 Jul 22. Chem Biomed Imaging. 2024. PMID: 39056064 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hanahan DJ. A Guide to Phospholipid Chemistry. New York: Oxford University Press; 1997.
-
- Wilton DC. Phospholipases. In: Vance DE, Vance JE, editors. Biochemistry of Lipids, Lipoproteins and Membranes. 5th Ed. Elsevier Science; 2008. pp. 305–329.
-
- Stefanski E, Pruzanski W, Sternby B, Vadas P. Purification of a soluble phospholipase A2 from synovial fluid in rheumatoid arthritis. J. Biochem. 1986;100:1297–1303. - PubMed
-
- Sved P, Scott KF, McLeod D, King NJC, Singh J, Tsatralis T, Nikolov B, Boulas J, Nallan L, Gelb MH, Sajinovic M, Graham GG, Russell PJ, Dong Q. Oncogenic action of secreted phospholipase A2 in prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2004;64:6934–6940. - PubMed
-
- Yamashita S-i, Ogawa M, Sakamoto K, Abe T, Arakawa H, Yamashita J-i. Elevation of serum group II phospholipase A2 levels in patients with advanced cancer. Clin. Chim. Acta. 1994;228:91–99. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

