Programmed death-1 affects suppressor of cytokine signaling-1 expression in T cells during hepatitis C infection
- PMID: 20883163
- PMCID: PMC2967821
- DOI: 10.1089/vim.2010.0010
Programmed death-1 affects suppressor of cytokine signaling-1 expression in T cells during hepatitis C infection
Abstract
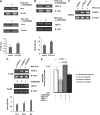
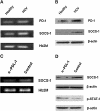
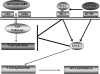
Chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection is associated with T-cell exhaustion that is mediated through upregulation of the PD-1 negative regulatory pathway. PD-1 expression is induced by HCV core protein, which also induces upregulation of SOCS-1, a key modulator that controls the Jak/STAT pathway regulating cytokine expression. To determine whether these two negative regulatory pathways are linked during T-cell signaling, SOCS-1 expression was examined by blocking the PD-1 pathway in T cells stimulated with anti-CD3/CD28 in the presence of HCV core protein. T cells isolated from healthy subjects or HCV-infected individuals were treated with anti-PD-1 or anti-PDL-1 antibodies in the presence or absence of HCV core protein, and SOCS-1 gene expression was detected by RT-PCR or immunoblotting, while T-cell functions were assayed by flow cytometric analyses. Both PD-1 and SOCS-1 gene expression were upregulated in healthy T cells exposed to HCV core protein, and blocking the PD-1 pathway downregulated SOCS-1 gene expression in these cells. Additionally, T cells isolated from chronically HCV-infected subjects exhibited increased PD-1 and SOCS-1 expression compared to healthy subjects, and SOCS-1 expression in T cells isolated from HCV-infected subjects was also inhibited by blocking PD-1 signaling; this in turn enhanced the phosphorylation of STAT-1, and improved the impaired T-cell proliferation observed in the setting of HCV infection. These data demonstrate that PD-1 and SOCS-1 are linked in dysregulating T-cell signaling during HCV infection, and their cross-talk may coordinately inhibit T-cell signaling pathways that lead to T-cell exhaustion during chronic viral infection.
Figures
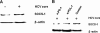

Similar articles
-
Cross-talk between programmed death-1 and suppressor of cytokine signaling-1 in inhibition of IL-12 production by monocytes/macrophages in hepatitis C virus infection.J Immunol. 2011 Mar 1;186(5):3093-103. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1002006. Epub 2011 Jan 24. J Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21263070
-
T cell dysfunction by hepatitis C virus core protein involves PD-1/PDL-1 signaling.Viral Immunol. 2007 Summer;20(2):276-87. doi: 10.1089/vim.2006.0096. Viral Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17603844
-
Tim-3 negatively regulates IL-12 expression by monocytes in HCV infection.PLoS One. 2011;6(5):e19664. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0019664. Epub 2011 May 26. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21637332 Free PMC article.
-
Costimulatory molecule programmed death-1 in the cytotoxic response during chronic hepatitis C.World J Gastroenterol. 2009 Nov 7;15(41):5129-40. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.5129. World J Gastroenterol. 2009. PMID: 19891011 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of SOCS proteins in the development of virus- induced hepatocellular carcinoma.Virol J. 2021 Apr 13;18(1):74. doi: 10.1186/s12985-021-01544-w. Virol J. 2021. PMID: 33849568 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Immune exhaustion and immune senescence: two distinct pathways for HBV vaccine failure during HCV and/or HIV infection.Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2013 Jun;61(3):193-201. doi: 10.1007/s00005-013-0219-0. Epub 2013 Feb 12. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2013. PMID: 23400275 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tim-3 pathway controls regulatory and effector T cell balance during hepatitis C virus infection.J Immunol. 2012 Jul 15;189(2):755-66. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1200162. Epub 2012 Jun 15. J Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22706088 Free PMC article.
-
Tim-3 alters the balance of IL-12/IL-23 and drives TH17 cells: role in hepatitis B vaccine failure during hepatitis C infection.Vaccine. 2013 Apr 26;31(18):2238-45. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2013.03.003. Epub 2013 Mar 14. Vaccine. 2013. PMID: 23499521 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating Tregs correlate with viral load reduction in chronic HBV-treated patients with tenofovir disoproxil fumarate.J Clin Immunol. 2011 Jun;31(3):509-20. doi: 10.1007/s10875-011-9509-7. Epub 2011 Feb 9. J Clin Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21305387
-
Tim-3 suppression combined with TLR3 activation enhances antiviral immune response in patients with chronic HCV infection.J Int Med Res. 2016 Aug;44(4):806-16. doi: 10.1177/0300060516647548. Epub 2016 Jun 21. J Int Med Res. 2016. PMID: 27329385 Free PMC article.
References
-
- King E. Trabue C. Yin D. Yao ZQ. Moorman JP. Hepatitis C: the complications of immune dysfunction. Exp Rev Clin Immunol. 2007;3:145–157. - PubMed
-
- Wedemeyer H. He XS. Nascimbeni M, et al. Impaired effector function of hepatitis C virus specific CD8+ T cells in chronic hepatitis C virus infection. J Immunol. 2002;169:3447–3458. - PubMed
-
- Lechmann M. Woitas RP. Langhans B, et al. Decreased frequency of HCV core-specific peripheral blood mononuclear cells with type 1 cytokine secretion in chronic hepatitis. Can J Hepatol. 1999;31:971–978. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

