Psychophysical stress increases the expression of phospho-CREB, Fos protein and neurokinin-1 receptors in superficial laminae of trigeminal subnucleus caudalis in female rats
- PMID: 20884322
- PMCID: PMC2967612
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neulet.2010.09.054
Psychophysical stress increases the expression of phospho-CREB, Fos protein and neurokinin-1 receptors in superficial laminae of trigeminal subnucleus caudalis in female rats
Abstract
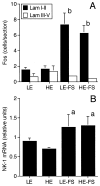
Psychological stress and estrogen status are risk factors to develop painful temporomandibular joint disorders (TMJD); however, the neural basis for this relationship is not known. This study tested the hypothesis that repeated forced swim stress and estradiol treatment alter the phosphorylation of cAMP responsive element-binding protein (pCREB) in trigeminal subnucleus caudalis (Vc), the initial site of sensory input from the TMJ. Ovariectomized female rats were given low or high dose estradiol and subjected to repeated forced swim stress for 3 days and on day 4 an intra-TMJ injection of mustard oil or vehicle was given. Forced swim alone increased the number of pCREB-positive neurons, independent of estradiol treatment or TMJ stimulation, in superficial and deep laminae of Vc. Forced swim also increased the number of Fos-positive neurons in superficial laminae and neurokinin-1 receptor mRNA in whole dorsal Vc, independent of estradiol treatment. These results indicated that persistent psychophysical stress alone was sufficient to increase the expression of pCREB and downstream regulated genes associated with enhanced excitability in the caudal medullary dorsal horn, a brainstem region thought to be critical for TMJD pain.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Estrogen status and psychophysical stress modify temporomandibular joint input to medullary dorsal horn neurons in a lamina-specific manner in female rats.Pain. 2013 Jul;154(7):1057-64. doi: 10.1016/j.pain.2013.03.009. Epub 2013 Mar 15. Pain. 2013. PMID: 23607965 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of persistent monoarthritis of the temporomandibular joint region on acute mustard oil-induced excitation of trigeminal subnucleus caudalis neurons in male and female rats.Pain. 2005 Sep;117(1-2):58-67. doi: 10.1016/j.pain.2005.05.013. Pain. 2005. PMID: 16043292
-
Morphine modulation of temporomandibular joint-responsive units in superficial laminae at the spinomedullary junction in female rats depends on estrogen status.Eur J Neurosci. 2008 Nov;28(10):2065-74. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2008.06488.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 19046387
-
Local group I mGluR antagonists reduce TMJ-evoked activity of trigeminal subnucleus caudalis neurons in female rats.Neuroscience. 2015 Jul 23;299:125-33. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2015.04.051. Epub 2015 Apr 29. Neuroscience. 2015. PMID: 25934040
-
The effects of estrogen on temporomandibular joint pain as influenced by trigeminal caudalis neurons.J Oral Sci. 2020 Mar 28;62(2):150-155. doi: 10.2334/josnusd.19-0405. Epub 2020 Mar 4. J Oral Sci. 2020. PMID: 32132330 Review.
Cited by
-
Preclinical models of deep craniofacial nociception and temporomandibular disorder pain.Jpn Dent Sci Rev. 2021 Nov;57:231-241. doi: 10.1016/j.jdsr.2021.10.002. Epub 2021 Nov 12. Jpn Dent Sci Rev. 2021. PMID: 34815817 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Temporomandibular joint-evoked responses by spinomedullary neurons and masseter muscle are enhanced after repeated psychophysical stress.Eur J Neurosci. 2012 Jul;36(1):2025-34. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2012.08100.x. Epub 2012 Apr 22. Eur J Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22519876 Free PMC article.
-
EXPRESS: Histone hyperacetylation modulates spinal type II metabotropic glutamate receptor alleviating stress-induced visceral hypersensitivity in female rats.Mol Pain. 2016 Jul 5;12:1744806916660722. doi: 10.1177/1744806916660722. Print 2016. Mol Pain. 2016. PMID: 27385724 Free PMC article.
-
CREB-regulated transcription coactivator 1 enhances CREB-dependent gene expression in spinal cord to maintain the bone cancer pain in mice.Mol Pain. 2016 Apr 8;12:1744806916641679. doi: 10.1177/1744806916641679. Print 2016. Mol Pain. 2016. PMID: 27060162 Free PMC article.
-
Estrogen status and psychophysical stress modify temporomandibular joint input to medullary dorsal horn neurons in a lamina-specific manner in female rats.Pain. 2013 Jul;154(7):1057-64. doi: 10.1016/j.pain.2013.03.009. Epub 2013 Mar 15. Pain. 2013. PMID: 23607965 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bereiter DA, Benetti AP. Amino acid release at the spinomedullary junction after inflammation of the TMJ region in male and female rats. Pain. 2006;126:175–183. - PubMed
-
- Bradesi S, Kokkotou E, Simeonidis S, Patierno S, Ennes HS, Mittal Y, McRoberts JA, Ohning G, McLean P, Marvizon JC, Sternini C, Pothoulakis C, Mayer EA. The role of neurokinin 1 receptors in the maintenance of visceral hyperalgesia induced by repeated stress in rats. Gastroenterology. 2006;130:1729–1742. - PubMed
-
- Carlezon WA, Jr, Duman RS, Nestler EJ. The many faces of CREB. Trends Neurosci. 2005;28:436–45. - PubMed
-
- Carlstrom L, Ke ZJ, Unnerstall JR, Cohen RS, Pandey SC. Estrogen modulation of the cyclic AMP response element-binding protein pathway. Effects of long-term and acute treatments. Neuroendocrinology. 2001;74:227–43. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

