Structural requirements for activation in alphaIIb beta3 integrin
- PMID: 20884611
- PMCID: PMC2992275
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.139667
Structural requirements for activation in alphaIIb beta3 integrin
Abstract
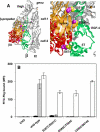
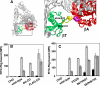
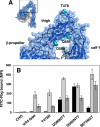
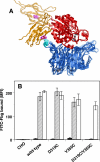
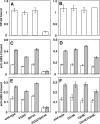
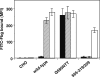
Integrins are postulated to undergo structural rearrangement from a low affinity bent conformer to a high affinity extended conformer upon activation. However, some reports have shown that a bent conformer is capable of binding a ligand, whereas another report has shown that integrin extension does not absolutely lead to activation. To clarify whether integrin affinity is indeed regulated by the so-called switchblade-like movement, we have engineered a series of mutant αIIbβ3 integrins that are constrained specifically in either a bent or an extended conformation. These mutant αIIbβ3 integrins were expressed in mammalian cells, and fibrinogen binding to these cells was examined. The bent integrins were created through the introduction of artificial disulfide bridges in the β-head/β-tail interface. Cells expressing bent integrins all failed to bind fibrinogen unless pretreated with DTT to disrupt the disulfide bridges. The extended integrins were created by introducing N-glycosylation sites in amino acid residues located close to the α-genu, where the integrin legs fold backward. Among these mutants, activation was maximized in one integrin with an N-glycosylation site located behind the α-genu. This extension-induced activation was completely blocked when the swing-out of the hybrid domain was prevented. These results suggest that the bent and extended conformers represent low affinity and high affinity conformers, respectively, and that extension-induced activation depends on the swing-out of the hybrid domain. Taken together, these results are consistent with the current hypothesis that integrin affinity is regulated by the switchblade-like movement of the integrin legs.
Figures
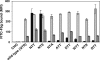
Similar articles
-
Membrane-proximal {alpha}/{beta} stalk interactions differentially regulate integrin activation.J Biol Chem. 2005 Jul 1;280(26):24775-83. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M409548200. Epub 2005 Apr 29. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 15863495
-
Effects of limiting extension at the alphaIIb genu on ligand binding to integrin alphaIIbbeta3.J Biol Chem. 2010 Jun 4;285(23):17604-13. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.107763. Epub 2010 Apr 2. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20363746 Free PMC article.
-
The novel S527F mutation in the integrin beta3 chain induces a high affinity alphaIIbbeta3 receptor by hindering adoption of the bent conformation.J Biol Chem. 2009 May 29;284(22):14914-20. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M809167200. Epub 2009 Mar 27. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19329429 Free PMC article.
-
Suppression of integrin activation by the membrane-distal sequence of the integrin alphaIIb cytoplasmic tail.Biochem J. 2004 Apr 15;379(Pt 2):317-23. doi: 10.1042/BJ20031753. Biochem J. 2004. PMID: 14723599 Free PMC article.
-
A naturally occurring point mutation in the beta3 integrin MIDAS-like domain affects differently alphavbeta3 and alphaIIIbbeta3 receptor function.Thromb Haemost. 2001 Dec;86(6):1425-34. Thromb Haemost. 2001. PMID: 11776310
Cited by
-
Redox-relevant aspects of the extracellular matrix and its cellular contacts via integrins.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2014 May 1;20(13):1977-93. doi: 10.1089/ars.2013.5294. Epub 2014 Jan 8. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2014. PMID: 24040997 Free PMC article. Review.
-
αIIbβ3 variants defined by next-generation sequencing: predicting variants likely to cause Glanzmann thrombasthenia.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Apr 14;112(15):E1898-907. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1422238112. Epub 2015 Mar 31. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 25827233 Free PMC article.
-
Autonomous conformational regulation of β3 integrin and the conformation-dependent property of HPA-1a alloantibodies.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Sep 25;115(39):E9105-E9114. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1806205115. Epub 2018 Sep 12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 30209215 Free PMC article.
-
In silico analysis of structural modifications in and around the integrin αIIb genu caused by ITGA2B variants in human platelets with emphasis on Glanzmann thrombasthenia.Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2018 Mar;6(2):249-260. doi: 10.1002/mgg3.365. Epub 2018 Jan 31. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2018. PMID: 29385657 Free PMC article.
-
The importance of N-glycosylation on β3 integrin ligand binding and conformational regulation.Sci Rep. 2017 Jul 5;7(1):4656. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-04844-w. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28680094 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Calderwood D. A., Zent R., Grant R., Rees D. J., Hynes R. O., Ginsberg M. H. (1999) J. Biol. Chem. 274, 28071–28074 - PubMed
-
- Vinogradova O., Velyvis A., Velyviene A., Hu B., Haas T., Plow E., Qin J. (2002) Cell 110, 587–597 - PubMed
-
- Kim M., Carman C. V., Springer T. A. (2003) Science 301, 1720–1725 - PubMed
-
- Frelinger A. L., 3rd, Cohen I., Plow E. F., Smith M. A., Roberts J., Lam S. C., Ginsberg M. H. (1990) J. Biol. Chem. 265, 6346–6352 - PubMed
-
- Du X. P., Plow E. F., Frelinger A. L., 3rd, O'Toole T. E., Loftus J. C., Ginsberg M. H. (1991) Cell 65, 409–416 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

