Paracrine stimulation of endothelial cell motility and angiogenesis by platelet-derived deoxyribose-1-phosphate
- PMID: 20884872
- PMCID: PMC7528120
- DOI: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.110.215855
Paracrine stimulation of endothelial cell motility and angiogenesis by platelet-derived deoxyribose-1-phosphate
Abstract
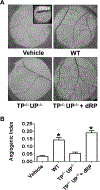
Objective: Micromolar concentrations of the proangiogenic metabolite deoxyribose-1-phosphate (dRP) were detected in platelet supernatants by mass spectrometry. In this study, we assessed whether the release of dRP by platelets stimulates endothelial cell migration and angiogenesis.
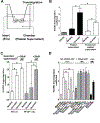
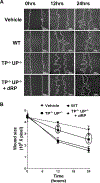
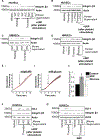
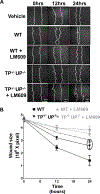
Methods and results: Protein-free supernatants from thrombin-stimulated platelets increased human umbilical vein endothelial cell migratory activity in transmigration and monolayer repair assays. This phenomenon was ablated by genetic silencing of dRP-generating uridine phosphorylase (UP) and thymidine phosphorylase (TP) or pharmacological inhibition of UP and restored by exogenous dRP. The stimulation of endothelial cell migration by platelet-derived dRP correlated with upregulation of integrin β(3), which was induced in a reactive oxygen species-dependent manner, and was mediated by the activity of the integrin heterodimer α(v)β(3). The physiological relevance of dRP release by platelets was confirmed in a chick chorioallantoic membrane assay, where the presence of this metabolite in platelet supernatants strongly induced capillary formation.
Conclusions: Platelet-derived dRP stimulates endothelial cell migration by upregulating integrin β(3) in a reactive oxygen species-dependent manner. As demonstrated by our in vivo experiments, this novel paracrine regulatory pathway is likely to play an important role in the stimulation of angiogenesis by platelets.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Autocrine amplification of integrin αIIbβ3 activation and platelet adhesive responses by deoxyribose-1-phosphate.Thromb Haemost. 2013 Jun;109(6):1108-19. doi: 10.1160/TH12-10-0751. Epub 2013 Mar 14. Thromb Haemost. 2013. PMID: 23494007 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomics identifies thymidine phosphorylase as a key regulator of the angiogenic potential of colony-forming units and endothelial progenitor cell cultures.Circ Res. 2009 Jan 2;104(1):32-40. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.108.182261. Epub 2008 Nov 20. Circ Res. 2009. PMID: 19023133
-
Direct Activation of NADPH Oxidase 2 by 2-Deoxyribose-1-Phosphate Triggers Nuclear Factor Kappa B-Dependent Angiogenesis.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2018 Jan 10;28(2):110-130. doi: 10.1089/ars.2016.6869. Epub 2017 Sep 18. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2018. PMID: 28793782 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of thrombin on interactions between beta3-integrins and extracellular matrix in platelets and vascular cells.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2003 Nov 1;23(11):1971-8. doi: 10.1161/01.ATV.0000093470.51580.0F. Epub 2003 Aug 28. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2003. PMID: 12947018 Review.
-
Thymidine phosphorylase, 2-deoxy-D-ribose and angiogenesis.Biochem J. 1998 Aug 15;334 ( Pt 1)(Pt 1):1-8. doi: 10.1042/bj3340001. Biochem J. 1998. PMID: 9693094 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Endothelial HO-1 induction by model TG-rich lipoproteins is regulated through a NOX4-Nrf2 pathway.J Lipid Res. 2016 Jul;57(7):1204-18. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M067108. Epub 2016 May 16. J Lipid Res. 2016. PMID: 27185859 Free PMC article.
-
Protective autophagy by thymidine causes resistance to rapamycin in colorectal cancer cells in vitro.Cancer Drug Resist. 2021 May 24;4(3):719-727. doi: 10.20517/cdr.2021.21. eCollection 2021. Cancer Drug Resist. 2021. PMID: 35582304 Free PMC article.
-
Thymidine Phosphorylase in Cancer; Enemy or Friend?Cancer Microenviron. 2016 Apr;9(1):33-43. doi: 10.1007/s12307-015-0173-y. Epub 2015 Aug 23. Cancer Microenviron. 2016. PMID: 26298314 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Platelet Response to Tissue Injury.Front Med (Lausanne). 2018 Nov 13;5:317. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2018.00317. eCollection 2018. Front Med (Lausanne). 2018. PMID: 30483508 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 couples cyclo-oxygenase-2 with pro-angiogenic actions of leptin on human endothelial cells.PLoS One. 2011 Apr 18;6(4):e18823. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0018823. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21533119 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brill A, Elinav H, Varon D. Differential role of platelet granular mediators in angiogenesis. Cardiovasc Res. 2004;63:226–235. - PubMed
-
- Brill A, Dashevsky O, Rivo J, Gozal Y, Varon D. Platelet-derived microparticles induce angiogenesis and stimulate post-ischemic revascularization. Cardiovasc Res. 2005;67:30–38. - PubMed
-
- Rhee JS, Black M, Schubert U, Fischer S, Morgenstern E, Hammes HP, Preissner KT. The functional role of blood platelet components in angiogenesis. Thromb Haemost. 2004;92:394–402. - PubMed
-
- Nurden AT, Nurden P, Sanchez M, Andia I, Anitua E. Platelets and wound healing. Front Biosci. 2008;13:3532–3548. - PubMed
-
- Langer HF, Gawaz M. Platelets in regenerative medicine. Basic Res Cardiol. 2008;103:299–307. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

